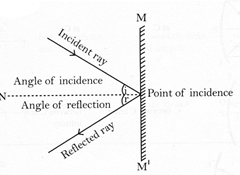
 The process of sending back the light rays which fall on the surface of an object, is called reflection of light.
Rules for obtaining images formed by concave mirrors
The process of sending back the light rays which fall on the surface of an object, is called reflection of light.
Rules for obtaining images formed by concave mirrors
 (a) 1728 (b) 1331
(c) 729 (d) 512
(e) None of these
Answer (b)
Explanation: Here the pattern is ________
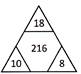
\[{{(18+10+8)}^{{}^{3}/{}_{2}}}=216\],
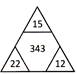
\[{{(15+12+22)}^{{}^{3}/{}_{2}}}=343\],
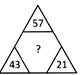
\[{{(57+43+21)}^{{}^{3}/{}_{2}}}=1331\]
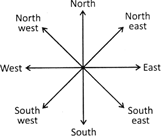
Direction Sense Problems
In such types of problems, we draw a diagram by using the given information. The following diagram shows all the Direction in a proper manner.
(a) 1728 (b) 1331
(c) 729 (d) 512
(e) None of these
Answer (b)
Explanation: Here the pattern is ________
\[{{(18+10+8)}^{{}^{3}/{}_{2}}}=216\],
\[{{(15+12+22)}^{{}^{3}/{}_{2}}}=343\],
\[{{(57+43+21)}^{{}^{3}/{}_{2}}}=1331\]
Direction Sense Problems
In such types of problems, we draw a diagram by using the given information. The following diagram shows all the Direction in a proper manner.
 Example:
If more...
Example:
If more...
 CHAPTER COVERAGE
CHAPTER COVERAGE
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
