 Green revolution
Green revolution
 Chapter Coverage
Chapter Coverage
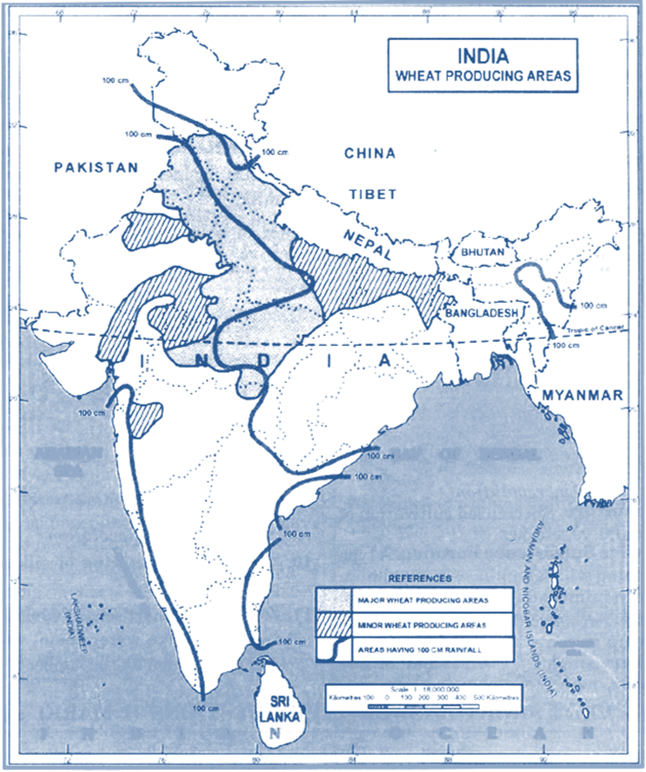 Chapter Coverage
Chapter Coverage
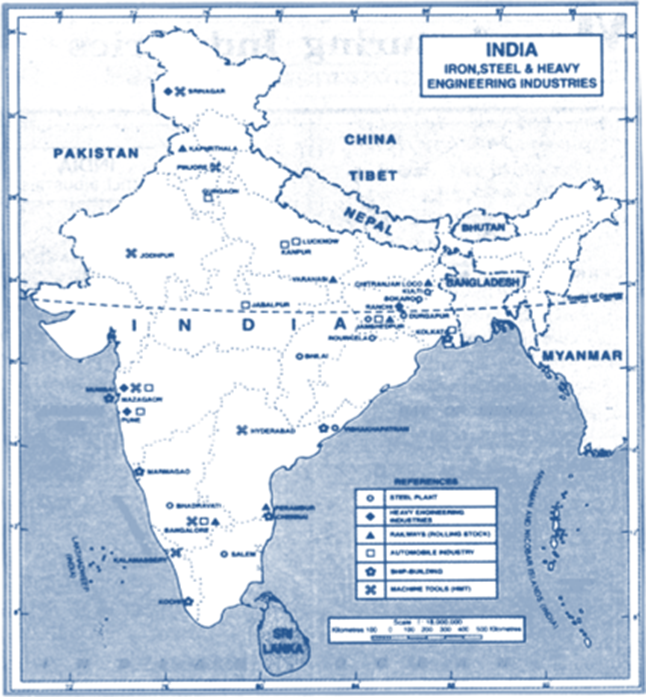 Important Terms And Concepts
Important Terms And Concepts
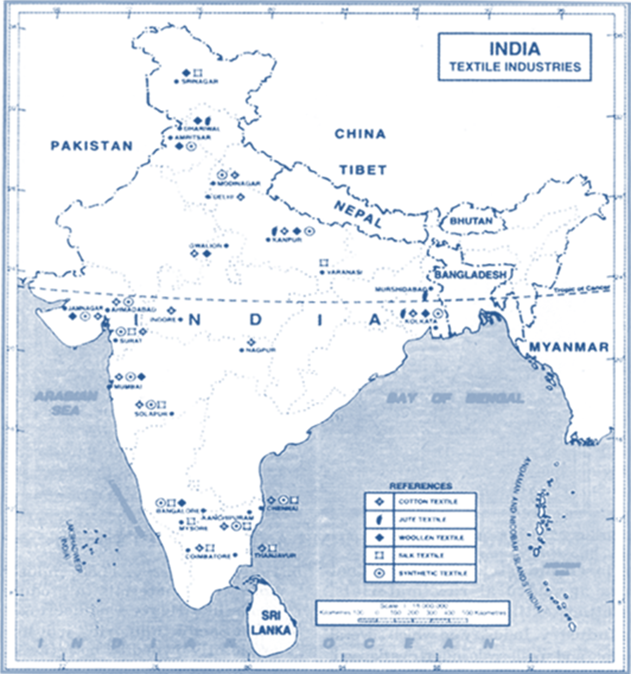 Chapter Coverage
Chapter Coverage
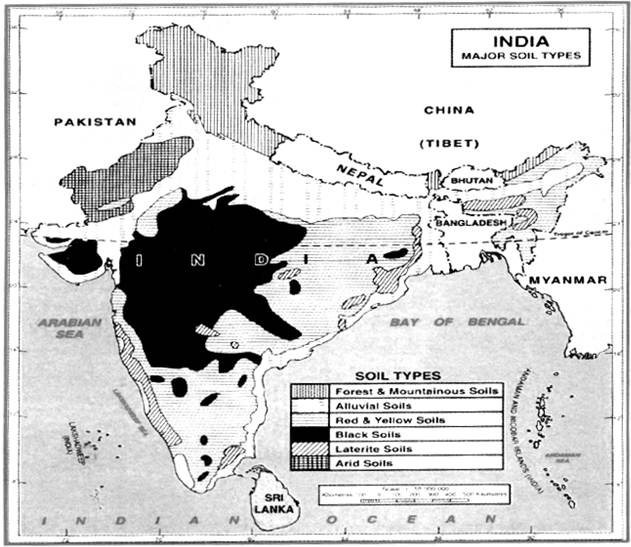 Chapter coverage
· Resources
· Classification of Resources
· Development of Resources
· Resource Planning
· Conservation of Resources more...
Chapter coverage
· Resources
· Classification of Resources
· Development of Resources
· Resource Planning
· Conservation of Resources more...
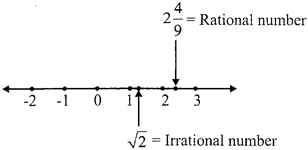 Note: Any number that can be represented on a number line is called a real number.
Note: Any number that can be represented on a number line is called a real number.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
