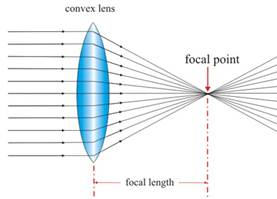
 Convex lens is the lens which is thicker at the center and thinner at the edge. It has two refracting surfaces. It is also called the converging lens as the ray of light converges at a point after refraction. The point, at which ray of light converges after refraction, is called the focus of the lens.
Convex lens is the lens which is thicker at the center and thinner at the edge. It has two refracting surfaces. It is also called the converging lens as the ray of light converges at a point after refraction. The point, at which ray of light converges after refraction, is called the focus of the lens.
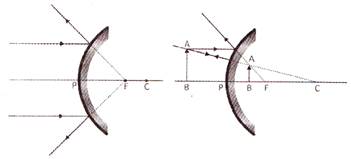 When the object is placed between P and F
When the object is placed in front of convex mirror, the image formed has following properties:
When the object is placed between P and F
When the object is placed in front of convex mirror, the image formed has following properties:
| S. NO. | Position of Object | more...
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |