Trigonometric Ratio
Trigonometric Ratio
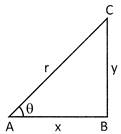 (i) \[\sin \theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}\,\,=\,\,\frac{y}{r}\]
(i) \[\sin \theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}\,\,=\,\,\frac{y}{r}\]
(ii) \[\cos \theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{Base}{Hypotenuse}\,\,=\,\,\frac{x}{r}\]
(iii) \[\tan \,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{Perpendicular}{Base}\,\,=\,\,\frac{y}{x}\]
(iv) \[\cos ec\,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{Hypotenuse}{Perpendicular}\,\,=\,\,\frac{r}{y}\]
(v) \[sec\,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{Hypotenuse}{Base}\,\,\,=\,\,\frac{r}{x}\]
(vi) \[\cot \,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{Base}{Perpendicular}\,\,\,=\,\,\frac{x}{y}\]
(i) \[\cos ec\,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{1}{\sin \,\theta }\,\,\]
(ii) \[sec\,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{1}{\cos \,\theta }\,\,\]
(iii) \[\cot \,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{1}{\tan \,\theta }\,\,\]
(iv) \[\tan \,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{\sin \,\theta }{\cos \,\theta }\,\,\]
(v) \[\cot \,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,\frac{\cos \,\theta }{\sin \,\theta }\,\,\]
(i) \[{{\sin }^{2}}+\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta \,\,=\,\,1\,\]
(ii) \[1\,\,+\,\,{{\tan }^{2}}\,\,\theta \,\,=\,\,{{\sec }^{2}}\,\,\theta \,\,for\,\,0{}^\circ \,\,\le \,\,\theta \,\,<\,\,90{}^\circ \]
(iii) \[1+{{\cot }^{2}}\theta =\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta \,\,for\,\,0{}^\circ <\theta \le 90{}^\circ \]
(i) \[sin\,\,\left( 90{}^\circ -\theta \right)=\,\,\cos \,\,\theta \]
(ii) \[\cos (90{}^\circ -\theta )\,\,=\,\,sin\theta
more...
