Sources of Energy
A source of energy is the one which can provide adequate amount of energy in a convenient form over a long period of time.
- Renewable sources of energy
Sources of energy which are being produced continuously in nature and are inexhaustible are called renewable sources of energy. The renewable sources of energy are: solar energy, wind energy, hydro energy, bio fuels (wood, biogas), hydrogen, energy from oceans and geothermal energy.
- Non-renewable sources of energy
Sources of energy which have been accumulated in nature over a very, very long period of time and cannot be quickly replaced when exhausted
more...
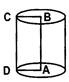
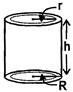 (i) Volume of material \[=\pi h({{R}^{2}}-r)\]
(ii) Curved surface area \[=2\pi h(R+r)\]
(iii) Total surface area \[=2\pi (R+r)(h+R-r)\]
(i) Volume of material \[=\pi h({{R}^{2}}-r)\]
(ii) Curved surface area \[=2\pi h(R+r)\]
(iii) Total surface area \[=2\pi (R+r)(h+R-r)\]
