Measurement of Length
There are various units for the measurement of the length. These are metre, centimeters, kilometers etc. The standard unit for the measurement of the length is metre.
1 centimeter = 10 millimeters
1 metre = 100 centimeters
1 kilometer = 1000 meters

A rope is 45 centimeters long. What will be the length of the rope in millimeters?
(a) 450 millimeters
(b) 4500 millimeters
(c) 405 millimeters
(d) 504 millimeters
Answer (a)
Explanations-
1 cm = 10 millimeters hence, 45 cm = 450 millimeters

What will be the length of each equal side of a triangle, if the sum of the length of its three sides is 15 cm?
(a) 4cm
(b) 5cm
(c) 3cm
(d) 2cm
Answer (b)
Explanation-
Each side\[=\frac{15}{3}=5\,cm\].

Conversion between Metre and Centimeter
1 metre\[~=\text{1}\times \text{1}00=\text{1}00\] centimeters
2 meters\[=\text{2}\times \text{1}00=\text{2}00\] centimeters
100 meters\[=\text{1}00\times \text{1}00=\text{1}0000\]centimeters

Convert 450 meters into centimeters.
(a) 45000cm
(b) 4500cm
(c) 2550cm
(d) 35500cm
Answer (a)
Explanations
1 m = 100 cm hence, 450 m = 45000 cm

What will be the 10thpart of a line segment of length 50 cm?
(a) 4cm
(b) 5cm
(c) 2cm
(d) 3cm
Answer (b)
Explanations
\[\text{1}{{0}^{\text{th}}}\]part of 50 cm\[=\frac{50}{10}=5\,cm\].

Conversion between Kilometer and Metre
1 kilometer\[=\text{1}\times \text{1}000=\text{1}000\]meters
2 kilometers\[=\text{2}\times \text{1}000=\text{2}000\] meters
100 kilometers\[=\text{1}00\times \text{1}000=\text{1}00000\]meters

Convert 9 km 500 m in meters.
(a) 8400 meters
(b) 9500 meters
(c) 7900 meters
(d) 8800 meters
Answer (b)
Explanations
9 km 500 m \[=(\text{9}\times \text{1}000+\text{5}00)\text{m}\] = 9500 m

A travels a distance of 56 km and B travels a distance of 39 km. Who travels the longer distance and by how much?
(a) A by 17 km (b) A by 19 km
(c) B by 19 km
(d) A by 20 km
Answer (a)
Explanations
Since 56 > 39 and\[\text{56}-\text{39}=\text{17}\]. Therefore, A travels longer distance by 17 km.

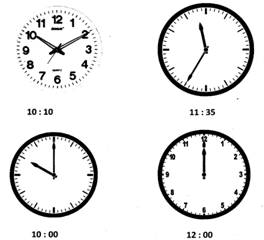 The small hand in a clock is for hour and the big hand is for the measurement of minute.
The small hand in a clock is for hour and the big hand is for the measurement of minute.