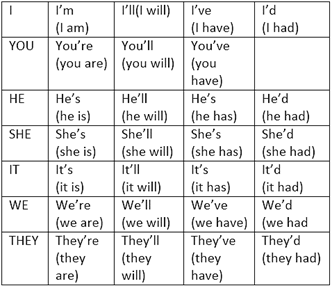
 For example: I am thinking can also be written as I'm thinking.
For example: I am thinking can also be written as I'm thinking.

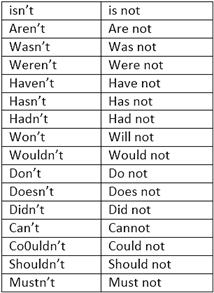
 Negative Contractions: When two words are put together to negate something, or to say no. No is contracted to ?n?t in the negative contractions. But the meaning does not change.
For example: I will not go can also be written as I won?t go. Negative contractions
Negative Contractions: When two words are put together to negate something, or to say no. No is contracted to ?n?t in the negative contractions. But the meaning does not change.
For example: I will not go can also be written as I won?t go. Negative contractions
 Amazing facts
Though in most of the words when they are contracted the first word remains the same but in will not, it is not contracted to wills? the word changes to won't
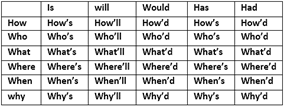
Words that ask a question are called interrogative words words. For example where, how, why, who, what.
Interrogative contractions
Amazing facts
Though in most of the words when they are contracted the first word remains the same but in will not, it is not contracted to wills? the word changes to won't
Words that ask a question are called interrogative words words. For example where, how, why, who, what.
Interrogative contractions

 But is used when we want to contrast the two sentences. For example He wanted to go. He could not go. Here by adding 'but' to the two sentences we get Contrast; He wanted to go, but he could not go.
Or is a connecting word that tells us that there is only one choice.
For example; you can go to the park. You can go to the mall.
But is used when we want to contrast the two sentences. For example He wanted to go. He could not go. Here by adding 'but' to the two sentences we get Contrast; He wanted to go, but he could not go.
Or is a connecting word that tells us that there is only one choice.
For example; you can go to the park. You can go to the mall.
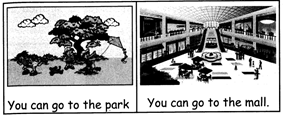 By adding the word Or We have; you can go To| the park or you can go to the mall.
This makes clear that there is only one choice. ·
Because is used when we want to give a reason for any action. The second part explains the reason for the first part. He could not attend the seminar because his flight got late. ·
When is used to tell about two ideas occurring at the same time.
For example, I love to go out when it's raining.
By adding the word Or We have; you can go To| the park or you can go to the mall.
This makes clear that there is only one choice. ·
Because is used when we want to give a reason for any action. The second part explains the reason for the first part. He could not attend the seminar because his flight got late. ·
When is used to tell about two ideas occurring at the same time.
For example, I love to go out when it's raining.
 I love to go out when it's raining. ·
While is also used to show two events happening at the same time. I was reading while travelling in the school bus.
I love to go out when it's raining. ·
While is also used to show two events happening at the same time. I was reading while travelling in the school bus.
 Amazing facts
There are a few conjunctions that are used as preposition and adverbs as well. For example after, before, since. ·
After is used to tell about relative time of two actions. I come out of the class, after I finished my paper.
Amazing facts
There are a few conjunctions that are used as preposition and adverbs as well. For example after, before, since. ·
After is used to tell about relative time of two actions. I come out of the class, after I finished my paper.
 Before is also used to tell about relative timing of two events. For example; before I could balance myself, I fell.
Before is also used to tell about relative timing of two events. For example; before I could balance myself, I fell.
 Before I could balance myself I fell.
Before I could balance myself I fell. 



 An is used before words that begin with vowels... a, e, I, o, u. or a vowel sound. For example An ice- cream, an egg, an inkpot. an
An is used before words that begin with vowels... a, e, I, o, u. or a vowel sound. For example An ice- cream, an egg, an inkpot. an




 'The' is used before some particular person or things. For example The Himalayas, the Bible, the Sun.
'The' is used before some particular person or things. For example The Himalayas, the Bible, the Sun.



 A and an suggest any person or thing. The suggests a particular person or thing. For example: A tree (any tree). The tree that is near my house. No article is used before proper nouns. For example Mr Smith is very hardworking. Snoopy is the name of his pet dog.
Remember
A and an suggest any person or thing. The suggests a particular person or thing. For example: A tree (any tree). The tree that is near my house. No article is used before proper nouns. For example Mr Smith is very hardworking. Snoopy is the name of his pet dog.
Remember
 In is used for large cities or countries or example: I am a native of India but I stop in France. ' I am a native of India but stay in France.
In is used for large cities or countries or example: I am a native of India but I stop in France. ' I am a native of India but stay in France.
 I am a native of india but stay in france.
On is used for smaller places. For example I am sitting on a chair.
I am a native of india but stay in france.
On is used for smaller places. For example I am sitting on a chair.
 Among is used when we talk of many objects or people. For example: He is among the best students of the school.
Among is used when we talk of many objects or people. For example: He is among the best students of the school.
 He is among the best students of the school Between is used when we talk of two things or people. For example: The Police Van got stuck between two buildings.
He is among the best students of the school Between is used when we talk of two things or people. For example: The Police Van got stuck between two buildings.
 A police van stuck between two buildings. By is used when we talk of a person doing something. For example: He is going by car.
A police van stuck between two buildings. By is used when we talk of a person doing something. For example: He is going by car.
 Suggested activity
You can show a picture and ask the child how things are placed in that picture.
Remember
The preposition ?with? is used in different ways. It is used to show ?using? for example: tom is playing with his ball. With can also be together with or in company of.
With is used when we talk of a tool used by a person. For example; A boy writing with a pencil. With can also be used to show company of. For example: Sheena went for cycling with her friends.
Suggested activity
You can show a picture and ask the child how things are placed in that picture.
Remember
The preposition ?with? is used in different ways. It is used to show ?using? for example: tom is playing with his ball. With can also be together with or in company of.
With is used when we talk of a tool used by a person. For example; A boy writing with a pencil. With can also be used to show company of. For example: Sheena went for cycling with her friends.

 We use Since when we talk of a fixed time. We use for when we want to show a period of time. For example. For how long have you been working here? Besides means addition to. For example: Besides he was quite hungry. Beside also means by the side of. For example: more...
We use Since when we talk of a fixed time. We use for when we want to show a period of time. For example. For how long have you been working here? Besides means addition to. For example: Besides he was quite hungry. Beside also means by the side of. For example: more... 
 ADVERBS OF HOW
ADVERBS OF HOW
 Adverbs of Frequency tell us how often the action isdone. For example:
He always goes to school. How often he goes toschool? Always answers the question. I seldom eat ice creams. How often you eat ice cream? Seldom answers the question.
ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY
Always never seldom often
Adverbs of Frequency tell us how often the action isdone. For example:
He always goes to school. How often he goes toschool? Always answers the question. I seldom eat ice creams. How often you eat ice cream? Seldom answers the question.
ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY
Always never seldom often

 He always goes to school. I seldom eat ice cream
ADVERBS OF QUANTITY
Quite very fully almost Absolutely entirely rather
The adverbs of quantity tell us how much? For example: The car accident almost crashed the cars. Here the word almost tells us the quantity of damage.
ADVERBS OF PLACE
Here There Upstairs Downstairs Nowhere
Adverbs of place tell us where the action is done. For example: a man is standing outside his car. The word outside tells us where the action is being done or is to be done.
He always goes to school. I seldom eat ice cream
ADVERBS OF QUANTITY
Quite very fully almost Absolutely entirely rather
The adverbs of quantity tell us how much? For example: The car accident almost crashed the cars. Here the word almost tells us the quantity of damage.
ADVERBS OF PLACE
Here There Upstairs Downstairs Nowhere
Adverbs of place tell us where the action is done. For example: a man is standing outside his car. The word outside tells us where the action is being done or is to be done.


 Possessive Adjectives - words like my, your, its, his and her tell us that something belongs to someone. They are called possessive adjectives. Words like our, your, and their show that something belongs to more than one person or group of people.
Possessive Adjectives - words like my, your, its, his and her tell us that something belongs to someone. They are called possessive adjectives. Words like our, your, and their show that something belongs to more than one person or group of people.
 Adjectives can also be used to compare two or more people, things or feelings. When we compare two things it is called comparative degree. We add ?er' to the word like *cold' becomes 'colder?
Adjectives can also be used to compare two or more people, things or feelings. When we compare two things it is called comparative degree. We add ?er' to the word like *cold' becomes 'colder?

 In some cases where the adjective ends in a Y we replace Y with 'ier?. For example. Nasty becomes nastier.
When we use adjectives to compare more than two people or things or feelings, it is called superlative degree. We add 'est? to a word to make it superlative degree.
Playtime
In some cases where the adjective ends in a Y we replace Y with 'ier?. For example. Nasty becomes nastier.
When we use adjectives to compare more than two people or things or feelings, it is called superlative degree. We add 'est? to a word to make it superlative degree.
Playtime





 QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
When you find yourself confused whether a sentence, has an action word or not, look at all words in the given sentence and ask yourself "is this something !that o person or an object can do"? For example: A boy is reading a book. Here the word reading is a verb or an action word. It suggests that an action is being done. If a verb is not used in a sentence the sentence seems to be incomplete.
For example when I say "I will school".
Does it have any meaning?
Now let us add' go 'to it, and write it as "I will go to school"
We find that just by adding an action word to the whole sentence we are able to add meaning to a sentence.
There are two forms of verbs. Doing words and Being Words. Doing words are words that tell us about some action taking place. For example. Jumping, Pulling.
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
When you find yourself confused whether a sentence, has an action word or not, look at all words in the given sentence and ask yourself "is this something !that o person or an object can do"? For example: A boy is reading a book. Here the word reading is a verb or an action word. It suggests that an action is being done. If a verb is not used in a sentence the sentence seems to be incomplete.
For example when I say "I will school".
Does it have any meaning?
Now let us add' go 'to it, and write it as "I will go to school"
We find that just by adding an action word to the whole sentence we are able to add meaning to a sentence.
There are two forms of verbs. Doing words and Being Words. Doing words are words that tell us about some action taking place. For example. Jumping, Pulling.

 BEING VERBS
Being verbs do not denote any action or doing, but they link the subject to the verb. The most common linking verb is to be
To Be: The various forms of it being, am, is, are, were, was, being, will be, has been.
Remember
BEING VERBS
Being verbs do not denote any action or doing, but they link the subject to the verb. The most common linking verb is to be
To Be: The various forms of it being, am, is, are, were, was, being, will be, has been.
Remember
 Suggested activity
Suggested activity


 Possessive pronouns: words used in place of nouns to show that something belongs to someone are called possessive pronouns. Yours, mine, theirs, hers and his are possessive pronouns
Possessive pronouns: words used in place of nouns to show that something belongs to someone are called possessive pronouns. Yours, mine, theirs, hers and his are possessive pronouns

 Objective pronouns: Words like me, us, them, whom her, him, it, and you are the object of the sentence. For example. Mr. Paul will buy a car for him
Demonstrative pronouns: Words such as this, that, these and those are called demonstrative pronouns. This is used when we want to tell of a single thing near us.
Objective pronouns: Words like me, us, them, whom her, him, it, and you are the object of the sentence. For example. Mr. Paul will buy a car for him
Demonstrative pronouns: Words such as this, that, these and those are called demonstrative pronouns. This is used when we want to tell of a single thing near us.



 ·
·
 Remember
Objective pronouns are the object and not the subject of the sentence.
Playtime
Copy a story or a passage from a book. Instead of writing the pronouns write the name of the subject. Always write the name in place of pronouns ask your friend to replace the nouns with the friend to do can the same for you.
Remember
Objective pronouns are the object and not the subject of the sentence.
Playtime
Copy a story or a passage from a book. Instead of writing the pronouns write the name of the subject. Always write the name in place of pronouns ask your friend to replace the nouns with the friend to do can the same for you. 
 Common Nouns: names given to common things around you like dog, cat, .school, mat are called common nouns.
Common Nouns: names given to common things around you like dog, cat, .school, mat are called common nouns.

 Proper Nouns: Names given to people, countries, cities, lanes, rivers, months, day?s pets are called proper nouns. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter. For example India: Qutub minor
Proper Nouns: Names given to people, countries, cities, lanes, rivers, months, day?s pets are called proper nouns. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter. For example India: Qutub minor

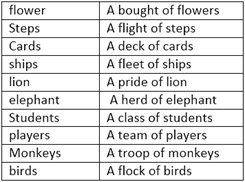
 Collective nouns: nouns that tell us about a group of things are called collective nouns. For example: a bouquet of flowers, a flight of steps,
Collective nouns: nouns that tell us about a group of things are called collective nouns. For example: a bouquet of flowers, a flight of steps, 
 Some common collective nouns
Some common collective nouns
 Singular nouns: singular nouns are names given to single things. For example a flower, a box
Singular nouns: singular nouns are names given to single things. For example a flower, a box

 Plural Nouns that are more than one in number are called plural nouns. Singular nouns can be changed into plural by:
Plural Nouns that are more than one in number are called plural nouns. Singular nouns can be changed into plural by:

 ·
Nouns that end with Y can be changed to plural by replacing Y with ies. For example Baby can be written as Babies. · If a word has a vowel before Y then only s is added to make it a plural. · If a word is ending with f then we can replace f with ves to make it a plural. For example Wolf becomes Wolves.
·
Nouns that end with Y can be changed to plural by replacing Y with ies. For example Baby can be written as Babies. · If a word has a vowel before Y then only s is added to make it a plural. · If a word is ending with f then we can replace f with ves to make it a plural. For example Wolf becomes Wolves. 
 ·
If a word ends with Sh, Ch, X, to make it into plural we add 'es* to it. For example Box becomes boxes.
·
If a word ends with Sh, Ch, X, to make it into plural we add 'es* to it. For example Box becomes boxes.

 Plural Possessive Nouns: Plural possessive nouns tell us about ownership by more than one person like Boys books, Girl's room.
Countable Nouns: A noun is countable if it can be counted like one biscuit, two biscuits. Countable nouns can be singular as well as plural.
Uncountable Nouns: A noun is uncountable if it cannot be counted. more...
Plural Possessive Nouns: Plural possessive nouns tell us about ownership by more than one person like Boys books, Girl's room.
Countable Nouns: A noun is countable if it can be counted like one biscuit, two biscuits. Countable nouns can be singular as well as plural.
Uncountable Nouns: A noun is uncountable if it cannot be counted. more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
