(1) Pyelonephritis : It is an inflammation of renal pelvis, calyces and interstitial tissue (G.pyelos = trough, tub; nephros = kidney; it is = inflammation). It is due to local bacterial infection. Bacteria reach here via urethra and ureter. Inflammation affects the countercurrent mechanism, and the victim fails to concentrate urine. Symptoms of the disease include pain in the back, and frequent and painful urination.
(2) Glomerulonephritis : It is the inflammation of glomeruli. It is caused by injury to the kidney, bacterial toxins, drug reaction, etc. Proteins and R.B.Cs pass into the filtrate.
(3) Cystitis : It is the inflammation of urinary bladder (G.kystis = bladder, - it is = inflammation). It is caused by bacterial infection. Patient has frequent, painful urination, often with burning sensation.
(4) Uremia : Uremia is the presence of an excessive amount of urea in the blood. It results from the decreased excretion of
more...
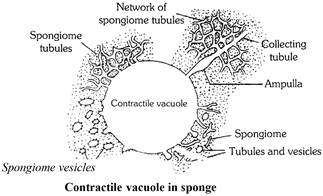 (3) Coelenterates : Hydra also lacks special excretory organs. The nitrogenous waste products like ammonia are removed through the general surface of the body by diffusion. Some nitrogenous waste products are also thrown along with indigestible matter through the mouth. more...
(3) Coelenterates : Hydra also lacks special excretory organs. The nitrogenous waste products like ammonia are removed through the general surface of the body by diffusion. Some nitrogenous waste products are also thrown along with indigestible matter through the mouth. more...
