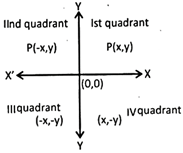
 x\[\to \] abscissa
y\[\to \] ordinate
x\[\to \] abscissa
y\[\to \] ordinate
 (b) Distance between the origin 0(0, 0) and the point P(x, y) is OP
\[op=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}\]
e.g.\[A=(5,3)\,\,\,B=(-2,5)\]
\[\therefore \,\,\,AB\]
\[=\sqrt{{{(-2-5)}^{2}}{{(5-3)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{49+4}=\sqrt{53}\]
(b) Distance between the origin 0(0, 0) and the point P(x, y) is OP
\[op=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}\]
e.g.\[A=(5,3)\,\,\,B=(-2,5)\]
\[\therefore \,\,\,AB\]
\[=\sqrt{{{(-2-5)}^{2}}{{(5-3)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{49+4}=\sqrt{53}\]
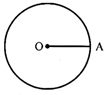 Let C (O, r) is a circle with centre 0 & radius r. A be any point it.
\[\therefore \] OA = radius of the circle
Let C (O, r) is a circle with centre 0 & radius r. A be any point it.
\[\therefore \] OA = radius of the circle
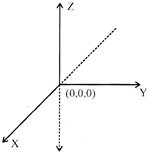 \[X'OX\xrightarrow{{}}x-axis\]
\[Y'OY\xrightarrow{{}}y-axis\]
\[Z'OZ\xrightarrow{{}}z-axis\]
Plane XOY is called xy plane
YOZ is called yz plane
and ZOX is called zx plane
In 3-D, there are 8 quadrents
Equation of x-axis be y= 0 & z =0
Equation of y-axis be x = 0 & z = 0
and equation of z-axis be x=0 & y=0
Note: In 3-D, a more...
\[X'OX\xrightarrow{{}}x-axis\]
\[Y'OY\xrightarrow{{}}y-axis\]
\[Z'OZ\xrightarrow{{}}z-axis\]
Plane XOY is called xy plane
YOZ is called yz plane
and ZOX is called zx plane
In 3-D, there are 8 quadrents
Equation of x-axis be y= 0 & z =0
Equation of y-axis be x = 0 & z = 0
and equation of z-axis be x=0 & y=0
Note: In 3-D, a more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
