Physical and Chemical Changes
All the substances have certain properties such as state (solid, liquid or gas), size, color, smell, temperature, shape, composition and structure etc.
When properties of a substance become different, we say that a change has taken place in it. Changes are taking place all around us. Some changes are beneficial to us and some are harmful to us. As for example ripening of fruits is a beneficial change. On the other hand rusting of iron is a harmful change.
Type of Changes
Physical changes
Chemical changes
Physical Change
Change in the physical properties (such as state, shape, size and colour) of a substance is called physical change. For example, breaking of glass, melting of ice, expanding of balloon, etc.
Characteristics of Physical Change
- No new substances are formed.
- Changes are temporary and can more...
 more...
more...
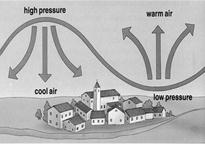 Wind is Produced Due to Uneven Heating on the Earth by the Sun
Uneven heating on the earth can take place by two situations:
Wind is Produced Due to Uneven Heating on the Earth by the Sun
Uneven heating on the earth can take place by two situations: