 FUNDAMENTALS
FUNDAMENTALS
 FUNDAMENTALS
FUNDAMENTALS
 WHAT IS SYMMETRY?
WHAT IS SYMMETRY?
 FUNDAMENTALS
FUNDAMENTALS
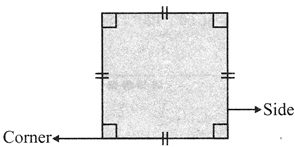 It has four sides and four comers, All its sides are of the same length.
(b) Rectangle.
It has four sides and four comers, All its sides are of the same length.
(b) Rectangle.
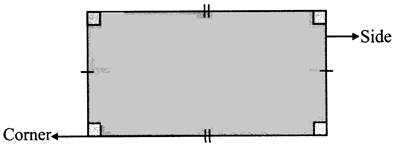 It has four sides and four comers. The opposite sides of more...
It has four sides and four comers. The opposite sides of more...
 FUNDAMENTALS
Collection and Tabulation of data:
FUNDAMENTALS
Collection and Tabulation of data:
| \[2x\] | Expression |
| \[2x+y\] |
more...
EXPONENT AND POWERS
POWER
\[\frac{{{a}^{m}}}{{{a}^{n}}}={{a}^{m}}-n\]
\[{{5}^{3}}\div {{5}^{2}}={{5}^{3}}-2\]
FUNDAMENTALS
Nutrition
Nutrition in Plants
All living beings need food to carry out various life processes. Food gives living beings the material to build and maintain their body.
Nutrition is the process by which an organism obtains its food and utilize them. The nutrition can be categorised mainly into two type's namely autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
Autotrophic Nutrition
Autotrophic organisms make their own food from simple raw materials available in their environment. Green plants, algae and some bacteria can produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis. The process of photosynthesis occurs only when plants or algae or some bacteria have green pigment, called chlorophyll in their cells. In the process of photosynthesis, the leaves of plants convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose or sugar and oxygen with the help of energy from the sun. Plants take in carbon dioxide from more...
Fibre to Fabric
Fibre
Fibre is a long and thin strand of a material. It can be categorised into two type’s namely natural fibre and manmade fibre.
Natural Fibre
Natural fibre is derived from plants and animals. Fibres such as cotton, flax and jute are derived from plants. Fibres such as silk and wool are derived from animals.
Plant Fibres
The fibres which we get from plants are called plant fibres.
Cotton, flax and jute are plant fibres.
Cotton: Cotton fibre is obtained from the seeds of the cotton plant.
Flax: Flax fibre is soft, lustrous and flexible. It is stronger than cotton fibre but is less elastic. The finer grade of flax fibre is used for producing linen fabrics such as damasks,
Lace and sheeting. The coarser grades of flax fibre are used for manufacturing twine and rope. Flax fibre more...
Physical and Chemical Changes
Heat
Heat is a form of energy and energy is the capacity to do work. This clearly indicates that work can be done with the help of heat.
Temperature
The decree of hotness and coldness is called the temperature of the body. The two common scales that are used to measure the temperature of the body are Celsius scale and Fahrenheit scale. On the Celsius scale, the melting point of ice is
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |