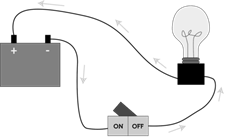
 more...
more...
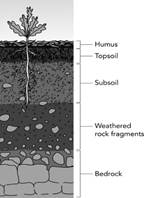 A-horizon: This is the uppermost layer of the soil. This layer is also called topsoil. It is dark in colour due to the presence of humus.
B-horizon: This layer is below the topsoil and is called subsoil. This soil is lighter in colour. The particles of this layer are coarser and porous. This layer does not contain much humans and thus not suitable for plants growth.
C-horizon: This layer is more...
A-horizon: This is the uppermost layer of the soil. This layer is also called topsoil. It is dark in colour due to the presence of humus.
B-horizon: This layer is below the topsoil and is called subsoil. This soil is lighter in colour. The particles of this layer are coarser and porous. This layer does not contain much humans and thus not suitable for plants growth.
C-horizon: This layer is more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
