Mensuration
Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures
Perimeter of geometrical figure is the sum of its sides. There are different types of geometrical figures. Figures are classified by their shapes and sizes. Area of a geometrical figure is its total surface area.
Perimeter and Area of a Triangle
- Perimeter of a triangle = Sum of the length of all sides.
- Area of a right triangle \[\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\times \text{Base}\times \text{Height}\]
- Perimeter of an equilateral triangle \[\text{=3}\times \text{Side}\]
- Area of an equilateral triangle \[\text{=}\frac{\sqrt{\text{3}}}{\text{4}}\times {{\text{(Side)}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Perimeter and Area of a Parallelogram
Parallelogram is a quadrilateral whose opposite sides are equal and parallel to each other.
In the given figure ABCD is a Parallelogram in which \[\text{AB}\parallel \text{CD,}\,\,\text{BC}\parallel \text{AD,}\,\,\text{AB}=\text{CD}\] and \[\text{AD=BC}\]
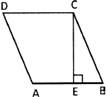
Perimeter of a Parallelogram = 2 (sum of two adjacent sides)
Hence,
more...
 Closed Circuit: When there is no gap in an electric circuit or the normal path of current has not been interrupted, the circuit is known as closed or complete circuit.
Open Circuit: When there is more...
Closed Circuit: When there is no gap in an electric circuit or the normal path of current has not been interrupted, the circuit is known as closed or complete circuit.
Open Circuit: When there is more...