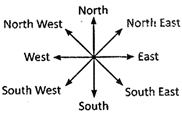
 Note: On paper North is always on the top while South is always at the bottom.
Concept of Turn more...
Note: On paper North is always on the top while South is always at the bottom.
Concept of Turn more...
 Properties of clock
Properties of clock
| more...
Number System
Learning Objective
Algebra
Learning Objectives
Geometry
Learning Objectives
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |