 Let us look at some examples to recognise the tenses.
Past Tense
1.
Gopal loved Sita.
2.
Rama was jumping in the garden.
3.
We had gone to the market yesterday.
4.
I had been painting the wall for two hours.
In these sentences, second form of verb, was, had etc.,
shows the past tense.
To recognise the past tense, we have to see the helping
verb in the sentence as underlined in the above sentences.
Present Tense
1.
Gopal loves Sita.
2.
Rama is jumping in the garden.
3.
They are playing.
4.
Conjunction
Conjunctions are words which join two sentences or two
words. Actually, you can say the conjunctive words act as a bridge in between two
sentences or words or numbers.
·
Example 1
1.
Entire world is made up of tiny particles and we are the part of
this.
2.
Two boys and three girls make five people.
3.
To say anything is easy but its implementation is hard.
4.
Do or die.
So, you can define conjunction as
follows:
The words which join two sentences or words or number.
The words, 'and, but, or' are the conjunctive words.
But you must give attention that conjunction must more...
Let us look at some examples to recognise the tenses.
Past Tense
1.
Gopal loved Sita.
2.
Rama was jumping in the garden.
3.
We had gone to the market yesterday.
4.
I had been painting the wall for two hours.
In these sentences, second form of verb, was, had etc.,
shows the past tense.
To recognise the past tense, we have to see the helping
verb in the sentence as underlined in the above sentences.
Present Tense
1.
Gopal loves Sita.
2.
Rama is jumping in the garden.
3.
They are playing.
4.
Conjunction
Conjunctions are words which join two sentences or two
words. Actually, you can say the conjunctive words act as a bridge in between two
sentences or words or numbers.
·
Example 1
1.
Entire world is made up of tiny particles and we are the part of
this.
2.
Two boys and three girls make five people.
3.
To say anything is easy but its implementation is hard.
4.
Do or die.
So, you can define conjunction as
follows:
The words which join two sentences or words or number.
The words, 'and, but, or' are the conjunctive words.
But you must give attention that conjunction must more...
 1.
Simple Prepositions:
Which shows simply the relation of a person or thing with
something else. For example: at, by, from
2.
Compound Preposition:
It is generally formed by prefixing a preposition to a
noun, an adjective or an adverb. For example: about, behind, underneath
3.
Phrase Prepositions:
They are the groups of words used as a single preposition.
For example: more...
1.
Simple Prepositions:
Which shows simply the relation of a person or thing with
something else. For example: at, by, from
2.
Compound Preposition:
It is generally formed by prefixing a preposition to a
noun, an adjective or an adverb. For example: about, behind, underneath
3.
Phrase Prepositions:
They are the groups of words used as a single preposition.
For example: more...
 1.
Adverb of Manner:
It shows how or in what manner.
For example:
Rama sleeps soundly.
The girl works hard.
2.
Adverb of Degree or Quantity:
It shows how much or in what degree.
For example:
He is too careless.
I am so glad.
3.
Adverb of Affirmation and Negation:
It shows confirmation.
For example:
He certainly went to Bhopal.
I do not know him.
4.
Adverb of Reason:
It shows the reasoning.
For example:
He therefore left home.
5.
Adverb more...
1.
Adverb of Manner:
It shows how or in what manner.
For example:
Rama sleeps soundly.
The girl works hard.
2.
Adverb of Degree or Quantity:
It shows how much or in what degree.
For example:
He is too careless.
I am so glad.
3.
Adverb of Affirmation and Negation:
It shows confirmation.
For example:
He certainly went to Bhopal.
I do not know him.
4.
Adverb of Reason:
It shows the reasoning.
For example:
He therefore left home.
5.
Adverb more...
 1.
Intransitive Verb:
The verb that does not need any
object to make a sentence meaningful is called intransitive verb.
For example:
Ram writes.
Neetu plays.
2.
Transitive Verb:
The verb that needs an object to
make a meaningful sentence is called transitive verb.
For example:
Neetu plays
lawn tennis.
Nita loves
me.
1.
Intransitive Verb:
The verb that does not need any
object to make a sentence meaningful is called intransitive verb.
For example:
Ram writes.
Neetu plays.
2.
Transitive Verb:
The verb that needs an object to
make a meaningful sentence is called transitive verb.
For example:
Neetu plays
lawn tennis.
Nita loves
me.
 (a) Transitive Verb
with Two Objects
There are two
objects with transitive verbs:
A person and
a thing
The person is an indirect and
the thing is a direct object.
(a) Transitive Verb
with Two Objects
There are two
objects with transitive verbs:
A person and
a thing
The person is an indirect and
the thing is a direct object.
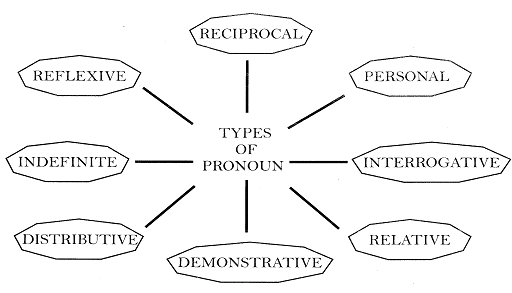 1.
Personal Pronoun:
The pronoun which indicates a person is called personal
pronoun.
For example: I am going
She is eating.
Personal Pronoun are used for first, second and third
person.
Various Forms and Functions of the Personal Pronoun:
1.
Personal Pronoun:
The pronoun which indicates a person is called personal
pronoun.
For example: I am going
She is eating.
Personal Pronoun are used for first, second and third
person.
Various Forms and Functions of the Personal Pronoun: