 \
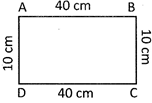
Perimeter of the quadrilateral \[ABCD=AB+BC+CD+DA\]
more...
\
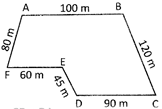
Perimeter of the quadrilateral \[ABCD=AB+BC+CD+DA\]
more...
 Basics terms of geometry
Basics terms of geometry
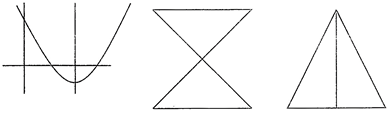 Line Symmetry
Line Symmetry
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
