Fractions
- A fraction is a part of a whole.
- In the fraction \[\frac{6}{7}\] ,6 is called the numerator and 7 is called the denominator.
- The denominator is the number of equal parts into which a whole is divided.
- The numerator is the number of parts considered of the whole.
Like fractions: Fractions with the same denominators.
e.g., \[\frac{4}{5},\frac{6}{5},\frac{3}{5}\]
Unlike fractions: Fractions with different denominators,
e.g.,\[\frac{1}{2},\frac{9}{4},\frac{3}{7}\]
Proper fractions: Fractions in which the denominator is greater than the numerator.
e.g.,\[\frac{2}{9},\frac{5}{6},\frac{2}{3}\]
Improper fractions: Fractions in which the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
e.g., \[\frac{9}{2},\frac{6}{5},\frac{3}{2},\frac{7}{7}\]
Mixed fractions: Fractions with a whole number part
more...
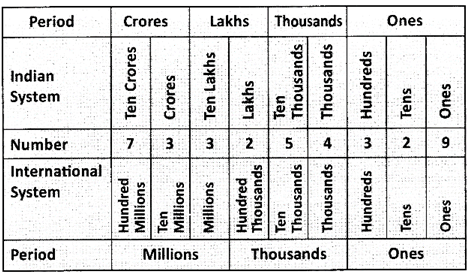 Indian System: 73, 32, 54,329
International System: 733,254,329
Note: A Comma is inserted each period in both the systems.
Indian System: 73, 32, 54,329
International System: 733,254,329
Note: A Comma is inserted each period in both the systems.