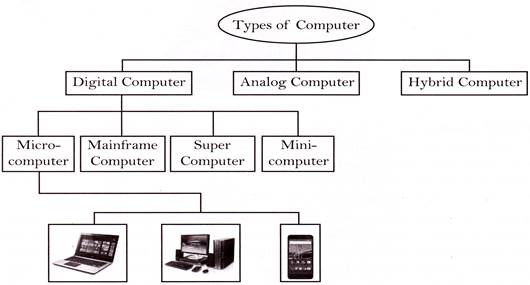
 Types of Computers
All the computers that are developed are not alike. They can have different designs and features. Computers can be as big as occupying a large building or as small as a laptop or may more...
Types of Computers
All the computers that are developed are not alike. They can have different designs and features. Computers can be as big as occupying a large building or as small as a laptop or may more...
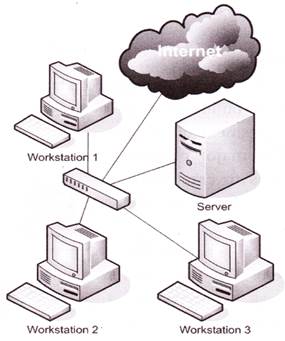 The Purpose of Networking
File and Data Sharing
It allows files to be shared instantaneously across the network with hundreds of users.
Resource Sharing
It allows the sharing of network resources such more...
The Purpose of Networking
File and Data Sharing
It allows files to be shared instantaneously across the network with hundreds of users.
Resource Sharing
It allows the sharing of network resources such more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
