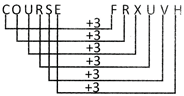
 more...
more...
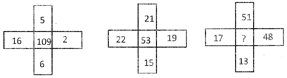 (a) 45 (b) 35
(c) 25 (d) 15
(e) None of these
Ans. (c)
Explanation: The pattern is
\[\to {{(16-6)}^{2}}+{{(5-2)}^{2}}=100+9=109\]
\[\to {{(22-15)}^{2}}+{{(21+19)}^{2}}=49+4=53\]
\[\to {{(17-13)}^{2}}+{{(51-48)}^{2}}=16+9=\]
2.
(a) 45 (b) 35
(c) 25 (d) 15
(e) None of these
Ans. (c)
Explanation: The pattern is
\[\to {{(16-6)}^{2}}+{{(5-2)}^{2}}=100+9=109\]
\[\to {{(22-15)}^{2}}+{{(21+19)}^{2}}=49+4=53\]
\[\to {{(17-13)}^{2}}+{{(51-48)}^{2}}=16+9=\]
2. 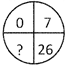 (a) 63 (b) 60
(c) 50 (d) 45
(e) None of these
Ans. more...
(a) 63 (b) 60
(c) 50 (d) 45
(e) None of these
Ans. more...
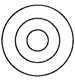 (b)
(b) 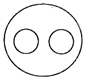 (c)
(c) 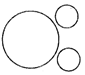 (d)
(d) 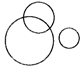 more...
more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
