Reproductive Health
Birth control is a term for several techniques and methods used to prevent fertilization or to interrupt pregnancy at various stages. Birth control techniques and methods include contraception , contragestion and abortion.
Contraception includes barrier methods, such as condoms or diaphragm, hormonal contraception, also known as oral contraception, and injectable contraceptives. Contragestives, also known as post-coital birth control, include intrauterine devices and what is known as the morning after pill.
The most common methods of hormonal contraception include the combined oral contraceptive pill and the minipill. Hormonal emergency contraception can be both contraceptive and contragestive.
Sterilization
Surgical sterilization is available in the form of tubal ligation for women and vasectomy for men. Although sterilization is considered a permanent procedure due to the uncertainty of reversal possibility, it
more...
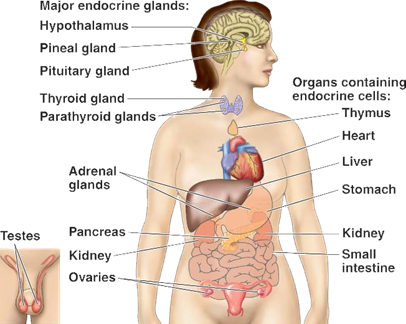 more...
more...

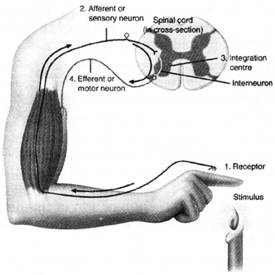 There are two types of reflex arc - autonomic reflex arc affecting inner organs and somatic reflex arc affecting more...
There are two types of reflex arc - autonomic reflex arc affecting inner organs and somatic reflex arc affecting more...
