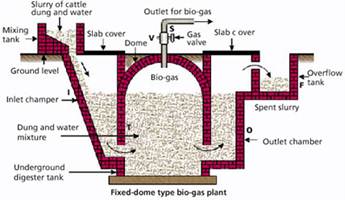
 The gases methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel. Biogas can be used as a fuel in any country for any heating purpose, such as cooking. It can also be used in anaerobic digesters, where it is typically more...
The gases methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel. Biogas can be used as a fuel in any country for any heating purpose, such as cooking. It can also be used in anaerobic digesters, where it is typically more...
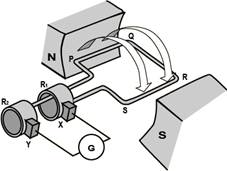 The coil is made up of large number of turns of insulated copper wire. The two ends P and S of the coil are connected more...
The coil is made up of large number of turns of insulated copper wire. The two ends P and S of the coil are connected more...
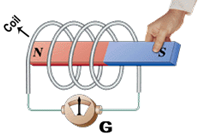 more...
more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
