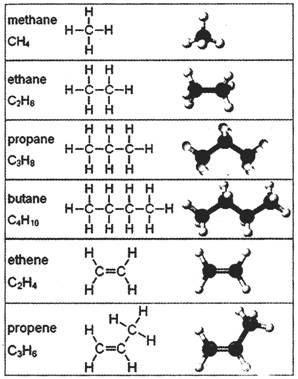
 Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) are the simplest of the hydrocarbon species and are composed entirely of single bonds and are saturated with hydrogen. The general formula for saturated hydrocarbons is\[{{\mathbf{C}}_{n}}{{\mathbf{H}}_{2n+2}}\]. Saturated hydrocarbons are the basis of petroleum fuels and are either found more...
Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) are the simplest of the hydrocarbon species and are composed entirely of single bonds and are saturated with hydrogen. The general formula for saturated hydrocarbons is\[{{\mathbf{C}}_{n}}{{\mathbf{H}}_{2n+2}}\]. Saturated hydrocarbons are the basis of petroleum fuels and are either found more...
| Sr.No. | more...

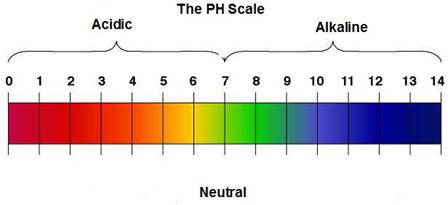 pH of some common samples
pH of some common samples
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |