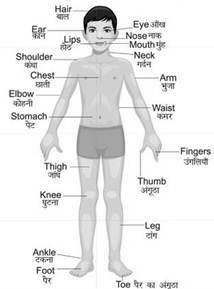
 Body parts
Human body consists of different parts. All of these parts have specific functions to perform. For example, we can see with the help of eyes and walk with the help of legs.
Flue Sense Organs
You know that we have five sense organs, which helps us to feel and know the world around us. Our sense organ and their functions are as follows:
Tongue
We can taste with the help of tongue. We can taste whether the food we eat is sweet, sour or salty with the help of taste buds located on the tongue.
Ear
We can hear the sounds with the help of ear. We can hear different sounds.
Eyes
We can see with the help of eyes. Whenever we see more...
Body parts
Human body consists of different parts. All of these parts have specific functions to perform. For example, we can see with the help of eyes and walk with the help of legs.
Flue Sense Organs
You know that we have five sense organs, which helps us to feel and know the world around us. Our sense organ and their functions are as follows:
Tongue
We can taste with the help of tongue. We can taste whether the food we eat is sweet, sour or salty with the help of taste buds located on the tongue.
Ear
We can hear the sounds with the help of ear. We can hear different sounds.
Eyes
We can see with the help of eyes. Whenever we see more...
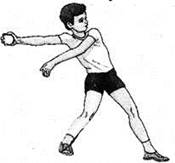 Boy exerts force to throw ball
Different Types of Motion
These are three types of motion.
Uniform Motion
If a body travels equal distance in equal interval of time then it is called uniform motion.
For example, a car travels first 30 kilometres in one hour and next 30 kilometres again in are hour and so on then we can say that car is in uniform motion.
Boy exerts force to throw ball
Different Types of Motion
These are three types of motion.
Uniform Motion
If a body travels equal distance in equal interval of time then it is called uniform motion.
For example, a car travels first 30 kilometres in one hour and next 30 kilometres again in are hour and so on then we can say that car is in uniform motion.
 more...
more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
