 Ascending Order of numbers: more...
Ascending Order of numbers: more...
 Step-2: Add the ONES first, then the TENs and finally the HUNDREDS.
more...
Step-2: Add the ONES first, then the TENs and finally the HUNDREDS.
more...
 we have, 12-3 =9 apples left.
Step - 2: Again give 1 apple to each boy.
we have, 12-3 =9 apples left.
Step - 2: Again give 1 apple to each boy.
 we have, 9-3=6 apples left.
Step - 3: Give 1 more apple to each boy
we have, 9-3=6 apples left.
Step - 3: Give 1 more apple to each boy
 more...
more...

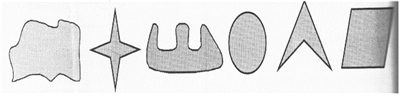
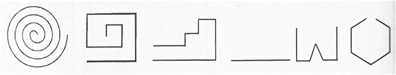
 Closed and Open figures:
Closed and Open figures:
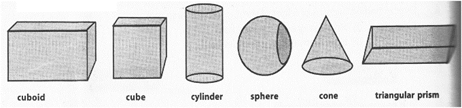
 Description of some basic shapes:
Description of some basic shapes:
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
