Laws of Chemical Combination
Various chemical reactions take place according to the certain laws, known as the Laws of chemical combination. These are as follows,
(1) Law of conservation of mass : It was proposed by Lavoisier and verified by Landolt. According to this law, Matter is neither created nor destroyed in the course of chemical reaction though it may change from one form to other. The total mass of materials after a chemical reaction is same as the total mass before reaction.
Example : A reaction between \[AgN{{O}_{3}}\] solution and \[KI\] solution.
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}_{(aq)}\,\,+\,\,K{{I}_{(aq)}}\,\,\xrightarrow{{}}\,\,AgI+\,NaN{{O}_{3}}_{(aq)}\] (yellow ppt.)
Mass of \[AgN{{O}_{3}}_{(aq)}\,\,+\,\,\text{Mass of }K{{I}_{(aq)}}\,\,\,=\,\,\,\text{Mass of the ppt}\text{. of }AgI\,\,+\,\,\text{Mass of }NaN{{O}_{3}}_{(aq)}\]
According to the modified statement of the law, The total sum of mass and energy of the system remains constant.
(2) Law of constant
more...
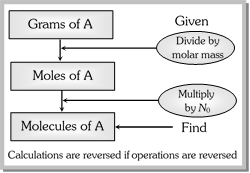 1 mole of a substance = \[6.022\times {{10}^{23}}\] species
The molar mass of a substance is the mass in grams of 1 mole of that substance.
\[\text{Mole of a substance }=\frac{\text{mass in grams}}{\text{molar mass}}\]
Under STP conditions when temperature is 273K and pressure is 1 atm, volume of one mole of more...
1 mole of a substance = \[6.022\times {{10}^{23}}\] species
The molar mass of a substance is the mass in grams of 1 mole of that substance.
\[\text{Mole of a substance }=\frac{\text{mass in grams}}{\text{molar mass}}\]
Under STP conditions when temperature is 273K and pressure is 1 atm, volume of one mole of more...
