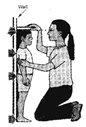
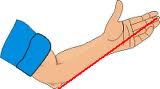
 Cubit Hand span
The metre is what we normally use for measuring lengths. Smaller lengths an measured in centimetres. Metre is written as m and centimetre as cm.
Measurement of Mass
Mass tells us how heavy or light an object is. We use weighing scales to find the mass of an object.
Just as we use metre for measuring more...
Cubit Hand span
The metre is what we normally use for measuring lengths. Smaller lengths an measured in centimetres. Metre is written as m and centimetre as cm.
Measurement of Mass
Mass tells us how heavy or light an object is. We use weighing scales to find the mass of an object.
Just as we use metre for measuring more...

 Plant Kingdom Animal Kingdom
The plant kingdom comprises of all the green plants present on the land, water and even those which are non-green in colour. The green colour of the plant is due to the presence of chlorophyll, which aid in photosynthesis. Nature has a wide variety of plants. Each variety has its more...
Plant Kingdom Animal Kingdom
The plant kingdom comprises of all the green plants present on the land, water and even those which are non-green in colour. The green colour of the plant is due to the presence of chlorophyll, which aid in photosynthesis. Nature has a wide variety of plants. Each variety has its more...
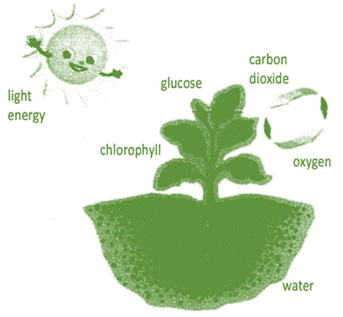 Plants, like other living things use atmospheric oxygen to breakdown glucose (food produced in photosynthesis) into carbon dioxide and water for the release of energy. This energy is used for its growth and maintenance. In plants, all living cells of root, stem and leaf take in oxygen independently and give out carbon dioxide and water. Hence in plants, there is little transport of gases, from one part to another, occurs Respiration in plants occur at a much more...
Plants, like other living things use atmospheric oxygen to breakdown glucose (food produced in photosynthesis) into carbon dioxide and water for the release of energy. This energy is used for its growth and maintenance. In plants, all living cells of root, stem and leaf take in oxygen independently and give out carbon dioxide and water. Hence in plants, there is little transport of gases, from one part to another, occurs Respiration in plants occur at a much more...
 Water Hyacinth
Water Hyacinth
 Non-Green Plant
Non-Green Plant



 Pine tree Deodar tree more...
Pine tree Deodar tree more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
