 Solution: more...
Solution: more...
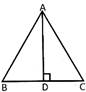 Area of the triangle ABC\[=\frac{1}{2}\times AD\times BC\]
Where BC is the base and AD is the height.
Area of the triangle ABC\[=\frac{1}{2}\times AD\times BC\]
Where BC is the base and AD is the height.
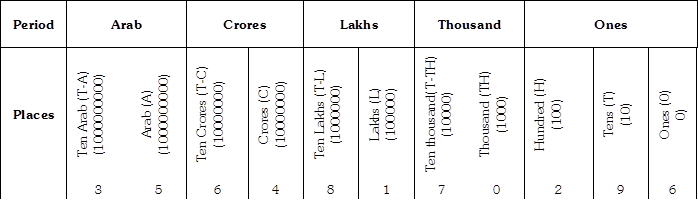 more...
more...
| Roman Numeral | more...
Operation on Numbers Addition and Subtraction
Introduction
In our daily life, we come across many activities when we need to apply the method of addition and subtraction. We are aware of numbers and number system. Now we will discuss two simple algebraic operations, that is, addition and subtraction.
Addition
Addition is one of the very common arithmetic operation used in mathematics. Addition is the operation to know the total quantity, when two or more than two quantities are taken together.
Operation on Numbers Multiplication and Division
Introduction
In this chapter we will study two important arithmetic operations "multiplication and division". Multiplication is repeated addition of a specific quantity, whereas division is a distribution of a quantity into some equal parts. Let us study them.
Multiplication
When a quantity is added to itself for a number of times, we use operation of multiplication to find the resulting quantity.
Factors and Multiples
Factors of a Number
All the numbers, which divide a certain number exactly, without leaving a remainder are called factors of that number.
For example:
Fractions and Decimals
Fraction
Fraction is used to indicate a part of a whole. Fraction is written as\[\frac{a}{b}\].
The top number in a fraction is called numerator and the bottom number is called denominator of the fraction. Hence in the given example 'a' is numerator and 'b' is denominator. Look at the shaded part in the following figures which has been represented by fractions:
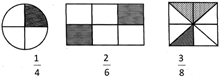
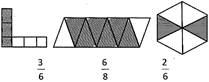
Unitary Method
Unitary Method
Unitary method is a method under which a calculation is carried out to find the value of the number of items, by first finding the value of one item.
From daily life experience, we know that when we increase the quantity of articles, their cost increases and when we decrease the quantity of articles, their cost decreases. In other words, more articles have more value and less articles have less value.
Note: In unitary method:
(i) To get more value we multiply.
(ii) To get less value we divide.
To solve the problems by unitary method we follow two steps:
Step 1: Get the value of a single unit.
Step 2: Then find the value of required units.
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |