
 QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
When a whole object or group is divided into equal parts, then each part is called a fraction of that whole.
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
When a whole object or group is divided into equal parts, then each part is called a fraction of that whole.
 Suppose, there is an apple and you want to divide it equally among 2 friends then equal pieces of the apple more...
Suppose, there is an apple and you want to divide it equally among 2 friends then equal pieces of the apple more...
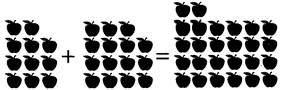 more...
more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
