Introduction
- The pollutants may be inorganic, biological or radiological in nature.
(i) Bio-degradable pollutants are domestic wastes which are rapidly decomposed by micro-organisms.
(ii) Non-biodegradable pollutants include chemicals, mercuric salts, lead compounds, pesticides, etc.
(iii) Natural pollution is caused by radioactive substances, volcanic eruptions, forests and mines fires floods, etc.
(iv) Artificial pollution is caused by industries, thermal plants, automobile, exhausts, sewage, etc.
Environment
- Environment: The conditions existing around animal or human life.
Atmosphere: The gaseous envelop surrounding the earth. It has been classified into following regions:-
(i) Stratosphere: The layer of the earth's atmosphere above the troposphere and below the mesosphere.
(ii) Troposphere: The lowest region of the atmosphere extending from earth's surface to the lower boundary of the stratosphere. In this region, human beings along with other organisms live. It contains water vapour and is greatly
more...
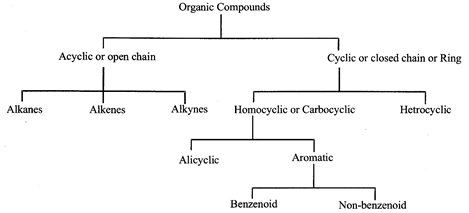 The existence of two or more chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but having different properties owing to different arrangement of atoms within the molecule is termed as isomerism
The existence of two or more chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but having different properties owing to different arrangement of atoms within the molecule is termed as isomerism