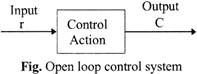
 For example: traffic light, tap of water etc.
Advantages: These systems are simple in construction & design; economic in nature; easy from the maintenance point of view, have high stability & are convenient to use when the output is difficult to measure.
Disadvantages: These systems are not accurate & reliable as the accuracy depends on the calibration of the inputs & their operation is affected due to the presence of non-linearities in the elements.
For example: traffic light, tap of water etc.
Advantages: These systems are simple in construction & design; economic in nature; easy from the maintenance point of view, have high stability & are convenient to use when the output is difficult to measure.
Disadvantages: These systems are not accurate & reliable as the accuracy depends on the calibration of the inputs & their operation is affected due to the presence of non-linearities in the elements.
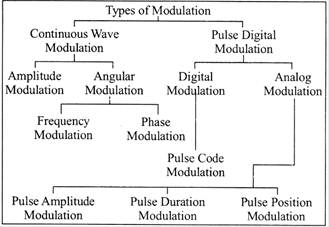 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
The method of varying amplitude of a high frequency carrier wave in accordance with the information to be transmitted, keeping the frequency and phase of the carrier wave unchanged is called Amplitude Modulation. The information is considered as the modulating signal and it is superimposed on the carrier wave by applying both of more...
AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
The method of varying amplitude of a high frequency carrier wave in accordance with the information to be transmitted, keeping the frequency and phase of the carrier wave unchanged is called Amplitude Modulation. The information is considered as the modulating signal and it is superimposed on the carrier wave by applying both of more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
