Work, Power, Energy
Work
Work done by the force is measured by the product of magnitude of force and the displacement of the point of application in the direction of force.
i.e., W=F.S
Work done = component of force in the direction of the displacement \[\times \] magnitude of displacement.
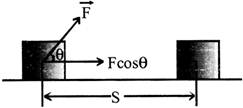
i.e., W= (F cos q) S=F S cos q or W=\[\overrightarrow{F.}\,\overrightarrow{S}\]
In terms of rectangular components, work done
W=\[\overrightarrow{F.}\,\overrightarrow{d}\]
\[W=(\hat{i}\,{{F}_{x}}+\hat{j}\,{{F}_{y}}+\hat{k}\,{{F}_{Z}}).(\hat{i}\,\,dx+\hat{j}\,dy+\hat{k}\,\,dz)\]
\[={{F}_{x}}dx+{{F}_{y}}dy+{{F}_{Z}}dz\]
Units of work
SI unit: joule (J). One joule of work is said to be done when a force of one newton displaces a body by one metre in the direction of force
\[1\,\,joule={{10}^{7}}erg\]
Dimensions of work:
Work = force, displacement
\[=[ML{{T}^{-2}}][L]=[M{{L}^{2}}{{T}^{-2}}]\]
Work Done in Pulling and Pushing an Object
\[F=\frac{\mu \,\,Mg}{\cos \theta +\mu \sin \theta }=force\,\,required\,to\,pull\,on\,object\] force required to pull an object \[W=F\,\,d=\frac{\mu \,\,Mg\,\,d}{\cos \theta +\mu
more...