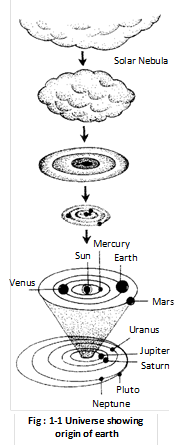
 The study of universe or cosmos is called Cosmology. Our earth belongs to the Solar system having nine stars called planets constantly rotating around a common Sun. On the basis of the order of the distance from the sun these planets include Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto while moon is a satellite of earth. The universe is made up of matter and energy and it was formed about 10 to more...
The study of universe or cosmos is called Cosmology. Our earth belongs to the Solar system having nine stars called planets constantly rotating around a common Sun. On the basis of the order of the distance from the sun these planets include Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto while moon is a satellite of earth. The universe is made up of matter and energy and it was formed about 10 to more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
