| A 1 | more...
Statements and Conclusions in Symbols
Introduction:
In this type of question there is a combination of two types of problem (i) coding (ii) critical reasoning. You have to solve these questions keeping in mind that you have to first solve the coding riddle before you begin solving the critical reasoning aspect of it. Given below are a full illustrations which will help you understand this type of question.
Example:
Directions (1 - 5): In the following questions, the symbols @, , *, $ and # are used with the following meaning:
\[A\,\,\#\,\,B\] means A is not greater than B.
\[A\,\$\,B\] means is neither smaller nor equal to B.
\[A\,?\,B\] means A is neither smaller nor greater than B.
\[A\,*\,B\] means A is neither greater nor equal to B.
\[A\,\,\,\,B\] means A is not smaller more...
Mathematical Operations
Introduction: This is a new type of verbal reasoning question which is being frequently asked in the various competitive examination. Here, a mathematical symbols is damaged with another symbol to confuse and then you are asked to solve an equation using the new instructions with changed symbols.
Example:
Sitting Arrangement
Introduction: Question of sitting Arrangement are based on a set of information containing certain conditions. Candidates are required to arrange the object either in a row or in a circle on the basis of given conditions. Information given in the question is presented in distorted form to create confusion and to test information's ability to analyse the information step by step in order to answer the question correctly. Following examples will help the students to understand this chapter clearly.
Example:
Blood Relations
Introduction: Blood relation test is information about blood relationship among the members of a family. In these questions, a chain process of two persons is given. On the basis of this the relations of the others are to be found out.
Types of Blood Relations
The relations may be divided into two types as given below:
(i) Blood relation from paternal side.
(ii) Blood relation from maternal side.
Now, we will discuss both kind of relations one by one.
Blood Relation From Paternal Side
This type of blood relation can further be subdivided into three types:
(a) Past generations of father
Example: Great grandfather, great grandmother, grandfather, grandmother etc.
(b) Parallel generations of father
Example: Uncles (Brothers of father), aunts (Sisters of father) etc.
(c) Future more...
Direction Sense Test
Concept of Direction: In general we make our concept of direction after seeing the position of the Sun. It is an universal truth that Sun rises in the East and goes down in the West. Thus, when we stand facing sunrise our front is called East, and our back is called west. At this position our left hand is in the northward and the right hand is in the southward. Let us see the following direction map to make the concept more clear.
Direction Map:
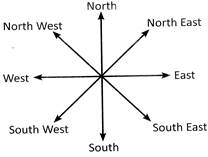 Note: On paper North is always on the top while South is always at the bottom.
Concept of Turn more...
Note: On paper North is always on the top while South is always at the bottom.
Concept of Turn more...
Syllogism
Introduction: Items based on Logical Reasoning are indispensable feature of all competitive examinations these days to test a candidate’s basic intelligence and aptitude. Syllogism is an important section of logical reasoning and hence a working knowledge of its rules is required on the part of the candidate. The term syllogism means inference or deduction drawn from the given statements.
The questions of syllogism can be solved with the help of Venn-diagrams and some rule devised with the help of analytical ability. Some people are of the opinion that Venn-diagram can be of great use for solving questions of syllogism. No doubt a few questions can be solved with the help of Venn-diagrams but van-diagrams alone do not help the students to solve variety of questions of syllogism. Even common sense also will not be much help in working out certain working out more...
Statement and Conclusion
Conclusion: Conclusions are inferences that can be drawn on the basis of the information given in the statement.
In these type of questions, a candidate is asked to decide whether a given inference follows or not in the light of the given statement or passage. For example,
Shravan – Let’s go to a restaurant.
Prakash – I have only Rs. 100.
What is your conclusion? – Shravan and Prakash cannot go to a restaurant. But why? Because nothing comes in Rs. 100 in a restaurant. But how do you know this? You don’t. You should keep in mind that never bring outside information into your reading of a decision making problem. Let’s understand how should we reach a conclusion. For this, follow the simple rules given below:
Rule 1
Don’t assume information, facts unless it is more...
Diagrammatic Puzzles
In these problems one has to count the geometrical figures in a given complex figure. A little bit of systematic approach is needed to get the correct number of the asked figure. The shape of geometrical figures must be clear in mind.
Example:
1. How many triangles are there in the figure given below?
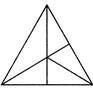 (a) 11 (b) 12
(c) 9 (d) 10
Ans. (b)
Explanation: The main triangle is: ABC - i.e. –1 triangle the simplest triangles are: ABE, AED, EBF, EDC and EFC i.e. -5 triangles
The triangle divided into two parts are: ABF, ABD, AEC and EBC i.e. - 4 triangles
Other triangles are: AFC and DBC i.e. - 2 triangles
So, the total more...
(a) 11 (b) 12
(c) 9 (d) 10
Ans. (b)
Explanation: The main triangle is: ABC - i.e. –1 triangle the simplest triangles are: ABE, AED, EBF, EDC and EFC i.e. -5 triangles
The triangle divided into two parts are: ABF, ABD, AEC and EBC i.e. - 4 triangles
Other triangles are: AFC and DBC i.e. - 2 triangles
So, the total more...
Complete of Incomplete Pattern
Introduction: This pattern are developed to judge your ability to comprehend geometric figures and diagrams. There also test your skills in perceiving the structure of a design and identifying the part missing in the main figure from the answer choices given, in the given figure a portion is left blank or incomplete.
In this type of problems, a figure or a matrix, containing a set of figures following a particular sequence or pattern is given, in which a part, generally a quarter is left blank. This problem figure is followed by four alternative figures. The candidate is required to select the one which best fits into the blank space of problem figure so as to complete the original pattern
Example:
1. Which one of the alternative figures will complete the figure pattern? more...
12th ClassArticles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |