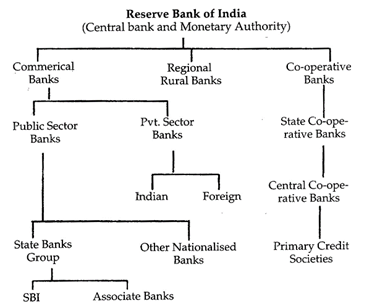
 COMMERCIAL BANKS
Commercial bank is an institution that accepts deposits, makes business loans and offers related services to general public and businessmen. Commercial banks in India are largely Indian public sector and private sector with a few foreign banks. The public sector banks account for more than 80 percent of the entire banking business in India occupying a dominant position in the commercial banking. These are a profit making institution owned by government or private or both.
There are currently 27 public sector banks in India out of which 19 are nationalised banks and 6 are SBI and its associate banks, and rest two are IDBI Bank and Bharatiya Manila Bank, which are categorised as other public sector banks. There are more...
COMMERCIAL BANKS
Commercial bank is an institution that accepts deposits, makes business loans and offers related services to general public and businessmen. Commercial banks in India are largely Indian public sector and private sector with a few foreign banks. The public sector banks account for more than 80 percent of the entire banking business in India occupying a dominant position in the commercial banking. These are a profit making institution owned by government or private or both.
There are currently 27 public sector banks in India out of which 19 are nationalised banks and 6 are SBI and its associate banks, and rest two are IDBI Bank and Bharatiya Manila Bank, which are categorised as other public sector banks. There are more...
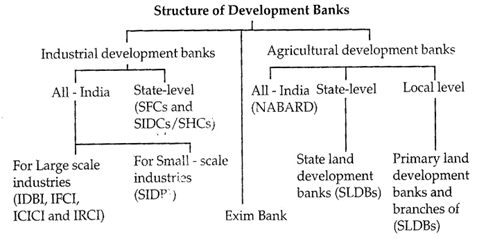
 Development banks in India are classified into following four groups;
Industrial Development Banks
They include for example. Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), and Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI). more...
Development banks in India are classified into following four groups;
Industrial Development Banks
They include for example. Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), and Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI). more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
