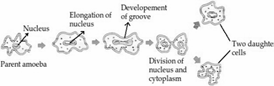
 Binary fission in Amoeba
Binary fission in Amoeba
 Sun
Solar is the closest star to the earth. Its average distance from the earth is about 150 million kilometers. It consists mainly of hydrogen and helium. Diameter of sun is about
1.4million km. The temperature at its surface is about\[6000{}^\circ C\].
Planets
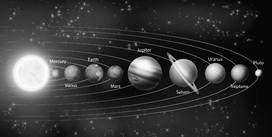
Based on the distances of planets from the sun they are as follows: Mercury, Venus,
Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. All the planets revolve around the sun in a fixed path called orbit. Planets which are close to the sun like Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called inner planets or terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, more...
Sun
Solar is the closest star to the earth. Its average distance from the earth is about 150 million kilometers. It consists mainly of hydrogen and helium. Diameter of sun is about
1.4million km. The temperature at its surface is about\[6000{}^\circ C\].
Planets
Based on the distances of planets from the sun they are as follows: Mercury, Venus,
Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. All the planets revolve around the sun in a fixed path called orbit. Planets which are close to the sun like Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called inner planets or terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, more...
| more...
Number System and Operations
In Mathematics we frequently come across different types of numbers. The different types of numbers are natural numbers, whole numbers, rational numbers, integers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. The natural number starts form 1 and goes to infinity Thus we can say that all the positive real numbers starting from 1 are called natural numbers. The whole numbers are all counting numbers together with 0. The set of all natural numbers, 0 and negative of all natural numbers including 0 are called integers. The rational numbers are the numbers which can be written in the form of\[\frac{p}{q}\], where p and q are integers and\[q\ne 0\].
Properties of Rational Number
Rational numbers satisfy various properties which are given below:
Closure Property
When we add two rational numbers the result is also a rational number, i.e. rational numbers are closed more...
Exponents
Exponents
Any number of the form \[{{x}^{n}},\]where n is a natural number and 'x' is a real number is called the exponents. Here n is called the power of the number x. Here x is the base and n is exponent (or index or power). Power may be positive or negative. For any rational number\[{{\left( \frac{x}{y} \right)}^{n}},\]n is called the power of the rational number.
So,\[{{\left( \frac{x}{y} \right)}^{n}}=\frac{{{x}^{n}}}{{{y}^{n}}}=\frac{x}{y}\times \frac{x}{y}\times \frac{x}{y}\times \frac{x}{y}\times \frac{x}{y}\times -----\times \frac{x}{y}\](n times)
Uses of Exponents
The exponents can be used for various purposes such as comparing large and small numbers, expressing large and small numbers in the standard forms. It is used to express the distance between any two celestial bodies which cannot be expressed in the form of normal denotation. It is also useful in writing the numbers in scientific notation. The size of the microorganisms is very-very more...
Algebra
An algebraic expression is an expression in one or more variables having different number of terms. Depending on the number of terms it may be monomials, binomials or polynomials. Like in the case of real numbers we can also
Use different mathematical operations on algebraic expression. Previously we have learnt to add and subtract the algebraic expression. In this chapter we will learn, how to multiply or divide the algebraic expression. We will also learn how to find the linear factors of the algebraic expression as in the case of real numbers and how to form a linear equation in one variable and to find its solution.
Multiplication of Algebraic Expressions
When two algebraic expressions are multiplied, the result obtained is called the product. The expressions being multiplied are called factors or multiplicands. While multiplying algebraic expressions first multiply numerical coefficients, then more...
Comparing Quantities
Variations
If two quantities are related with each other in such a way that change in one quantity will produce the corresponding change in the other quantity then they are said to be in variations. The variation may be that if we increase or decrease the one quantity then other quantity may also increase or decrease and vice-versa. If increase in one quantity results in the corresponding increase or decrease in other quantity then it is called direct variation and if increase in one quantity will result in to decrease in other quantity or vice-versa then it is called indirect variation.
For example increase in the cost with the increase in quantity is a direct variation whereas decrease in the time taken for a work with increase in the number of workers is an inverse variation.
Direct more...
Geometry
Polygon
Any figure bounded by three or more line segments is called a polygon. A regular polygon is one in which all sides are equal and all angles are equal. A regular polygon can be inscribed in a circle. The name of polygons with three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine and ten sides are respectively triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, heptagon, octagon, nonagon and decagon.
Convex Polygon
In a convex polygon, a line segment between two points on the boundary never goes outside the polygon. More precisely, in a convex polygon no internal angle can be more than\[180{}^\circ \].
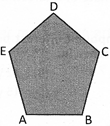 Convex polygon
Concave Polygon
In a concave polygon, a line segment between two points on the boundary goes outside the polygon.
or
In a concave polygon atleast one of the interior angle is more...
Convex polygon
Concave Polygon
In a concave polygon, a line segment between two points on the boundary goes outside the polygon.
or
In a concave polygon atleast one of the interior angle is more...
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |