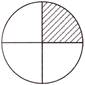
 Solution: \[\frac{1}{4}\]
Like Fraction
The fractions, which have the same denominators are called like fractions.
Example:
Solution: \[\frac{1}{4}\]
Like Fraction
The fractions, which have the same denominators are called like fractions.
Example:
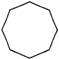 (a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 8 (d) 16
(e) None of these
Answer more...
(a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 8 (d) 16
(e) None of these
Answer more...
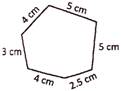 Solution: Perimeter of the figure =
\[4\text{ }cm+3\text{ }cm+4\text{ }cm+2.5\text{ }cm+5\text{ }cm+5\text{ }cm\]\[=23.50\text{ }cm.\]
Perimeter of the Triangles
A triangles has three sides. Perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its all the three sides.
Solution: Perimeter of the figure =
\[4\text{ }cm+3\text{ }cm+4\text{ }cm+2.5\text{ }cm+5\text{ }cm+5\text{ }cm\]\[=23.50\text{ }cm.\]
Perimeter of the Triangles
A triangles has three sides. Perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its all the three sides.
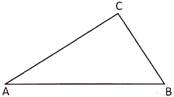 Perimeter of the triangle \[ABC=AB+BC+CA\]
Perimeter of the triangle \[ABC=AB+BC+CA\]
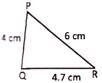 Solution: Perimeter of the triangle PQR
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
=4\text{ }cm+4.7\text{ }cm+6\text{ }cm \\
=14.7\text{ }cm \\
\end{array}\]
Perimeter of the Quadrilateral
Perimeter of more...
Solution: Perimeter of the triangle PQR
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
=4\text{ }cm+4.7\text{ }cm+6\text{ }cm \\
=14.7\text{ }cm \\
\end{array}\]
Perimeter of the Quadrilateral
Perimeter of more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
