 more...
more...
| more...
VOCABULARY
Learning Objectives
GRAMMAR
Learning Objectives
Motion
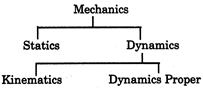
In the physical world, one of the most common phenomena is motion. The branch of Physics, which deals with the behavior of moving objects, is known as mechanics. Mechanics is further divided into two sections namely Kinematics and Dynamics.
Kinematics deals with the study of motion without taking into account the cause of motion.
Scalar Quantities: Physical quantities which have magnitude only and no direction are called scalar quantities.
Example: Mass, speed, volume, 'work, time, power, energy etc.
Vector Quantities: Physical quantities which have magnitude and direction both are called vector quantities.
Example: Displacement, velocity. Acceleration, Force, Momentum, torque etc.
Electric current though has a direction is a scalar quantity because it does not obey triangle law.
Distance: Distance is the length of actual path covered by a moving object in a given time interval. more...
Work, Energy and Power
Work
If a body gets displaced when a force acts on it, work is said to be done. Work is measured by the product of force and displacement of the body along the direction of force,
If a body gets displaced by S when a force F acts on it, then the work \[\operatorname{W}= F\,S cos\theta \]
Where \[\theta \] = angle between force and displacement.
If both force and displacement are in the same direction/ then W = FS.
Work is a scalar quantity and its SI unit is joule.
Energy
Capacity of doing work by a body is called its energy.
Sound
Sound is a wave caused by the movement of particles that travels through air or water similar to the ripples on a pond or the ocean waves you might see on a beach. A wave can be described as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location is called wave. There are two types of waves: Mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves.
Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are waves travelling through a vacuum and do not require a medium in order to transport their energy (propagation) e.g. Light.
Mechanical Waves
'Mechanical waves are waves which require a medium for propagation or to transport their energy from one point to another. It is of two types.
Longitudinal Wave: A mechanical waves in which the particles and the energy move in the more...
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |