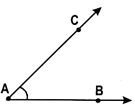
 The angle formed by the two rays \[\overline{AB}\,\,and\,\,\overline{AC}\text{ }is\text{ }\angle BAC\text{ }or\text{ }\angle CAB.~\]called \[\overline{AB}\,\,and\,\,\overline{AC}\]are called the arms and the common initial point ‘A’ is called the vertex of the angle.
The angle formed by the two rays \[\overline{AB}\,\,and\,\,\overline{AC}\text{ }is\text{ }\angle BAC\text{ }or\text{ }\angle CAB.~\]called \[\overline{AB}\,\,and\,\,\overline{AC}\]are called the arms and the common initial point ‘A’ is called the vertex of the angle.
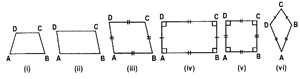 (i) Trapezium:
(a) A quadrilateral having exactly one pair more...
(i) Trapezium:
(a) A quadrilateral having exactly one pair more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
