| 8 | Y | |
| X | ||
| 4 |
9 more...
Learning Objectives
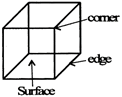 Example 1:
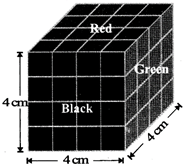
A cube of each side 4 cm, has been painted black, red and green on pairs of opposite faces. It is then cut into small cubes of each side 1 cm.
Example 1:
A cube of each side 4 cm, has been painted black, red and green on pairs of opposite faces. It is then cut into small cubes of each side 1 cm.
 more... more...
Learning Objective
 INTRODUCTION
Wastewater needs to be treated before it can be reused, or released into a water body. Wastewater has many impurities and these impurities should be removed by water treatment. Wastewater from households is treated at a treatment plant to remove the physical, biological and chemical matter. In the physical process, wastewater is filtered to remove large impurities. For example: Take a funnel. Place a filter paper in the funnel and wet it with water. Then add some sand, fine gravel and medium gravel into the funnel. These are layers for the filtration of water. Now pour wastewater into the funnel and collect clean water. Repeat the same more...
INTRODUCTION
Wastewater needs to be treated before it can be reused, or released into a water body. Wastewater has many impurities and these impurities should be removed by water treatment. Wastewater from households is treated at a treatment plant to remove the physical, biological and chemical matter. In the physical process, wastewater is filtered to remove large impurities. For example: Take a funnel. Place a filter paper in the funnel and wet it with water. Then add some sand, fine gravel and medium gravel into the funnel. These are layers for the filtration of water. Now pour wastewater into the funnel and collect clean water. Repeat the same more...
Learning Objectives
 A forest
INTRODUCTION
The forest is a complex ecosystem consisting mainly of trees that have formed a buffer for the earth to protect life forms. The trees which make up the main area of the forest create a special environment which, in turn, affects the kinds of animals and plants that can exist in the forest. Forests can be broadly classified into many types, some of which are the Taiga type (consisting of pines, spruce, etc.) the mixed temperate forests with both coniferous an deciduous trees, the temperate forests, the sub tropical forests, the tropical more...
A forest
INTRODUCTION
The forest is a complex ecosystem consisting mainly of trees that have formed a buffer for the earth to protect life forms. The trees which make up the main area of the forest create a special environment which, in turn, affects the kinds of animals and plants that can exist in the forest. Forests can be broadly classified into many types, some of which are the Taiga type (consisting of pines, spruce, etc.) the mixed temperate forests with both coniferous an deciduous trees, the temperate forests, the sub tropical forests, the tropical more...
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
Transportation in unicellular organisms
 TRANSPORTATION IN UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS
In unicellular organisms, transportation of substances happens through diffusion and osmosis. Gases move in and out of the cell by diffusion. Other substances more...
TRANSPORTATION IN UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS
In unicellular organisms, transportation of substances happens through diffusion and osmosis. Gases move in and out of the cell by diffusion. Other substances more...
Learning Objectives
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |