 more...
more...

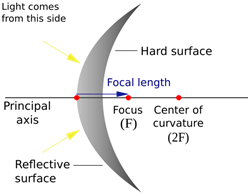 Fig.(1) Virtual image (In convex mirror) Fig.(2) more...
Fig.(1) Virtual image (In convex mirror) Fig.(2) more...
 Fig. (1) Side view of convex lens more...
Fig. (1) Side view of convex lens more...

 Sand clock is one of the instruments, which was used earlier to more...
Sand clock is one of the instruments, which was used earlier to more...
 Displacement is the distance between initial point from where object started to move and the final point where the object stopped. Displacement shows finally the object in which direction and at how far from the initial place sifted. Therefore displacement shows direction as well as distance. And it is a vector more...
Displacement is the distance between initial point from where object started to move and the final point where the object stopped. Displacement shows finally the object in which direction and at how far from the initial place sifted. Therefore displacement shows direction as well as distance. And it is a vector more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
