 Do you know?
The right lung is slightly larger than the left. The highest recorded sneeze speed is 165 km/hour.
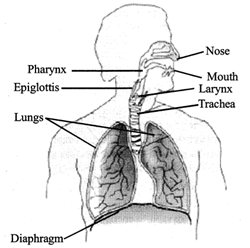
RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS
Respiration
The biological process in which food is utilized to produce energy is called respiration. Respiration is necessary for survival of the living beings. A living being cannot survive even for a few seconds, without respiration. During respiration, it is mainly the carbohydrate which is oxidized to produce energy. This can be shown by following equation:
Carbohydrate + Oxygen\[\to \]Carbon dioxide + Water + more...
Do you know?
The right lung is slightly larger than the left. The highest recorded sneeze speed is 165 km/hour.
RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS
Respiration
The biological process in which food is utilized to produce energy is called respiration. Respiration is necessary for survival of the living beings. A living being cannot survive even for a few seconds, without respiration. During respiration, it is mainly the carbohydrate which is oxidized to produce energy. This can be shown by following equation:
Carbohydrate + Oxygen\[\to \]Carbon dioxide + Water + more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
