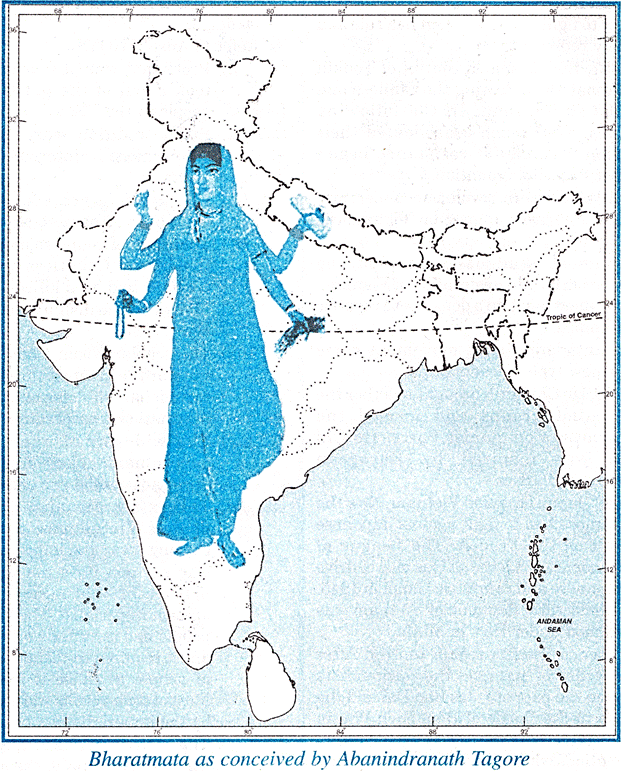
 CHAPTER COVERAGE
CHAPTER COVERAGE
| (i) Establishment of silk routes by China connecting China with the west. Other routes followed enabling explorers, traders, missionaries to travel which led to interaction among countries. | |
|
(ii) Discovery of sea routes to India and the Americas by more...
The Making of a Global World
IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS
The Making of a Global World
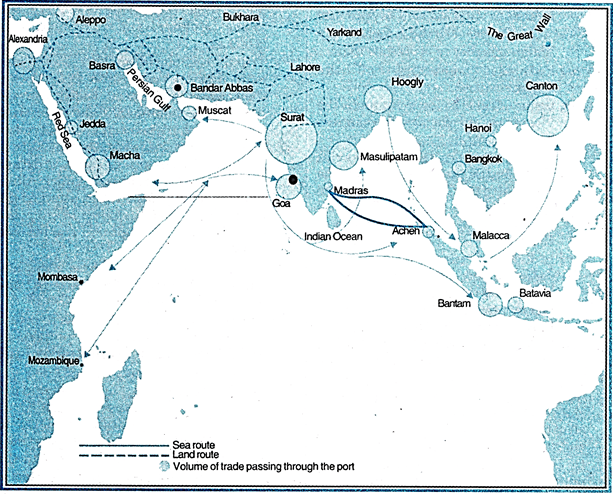 CHAPTER COVERAGE
CHAPTER COVERAGE
The Age of Industrialisation
IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS
The Age of Industrialisation
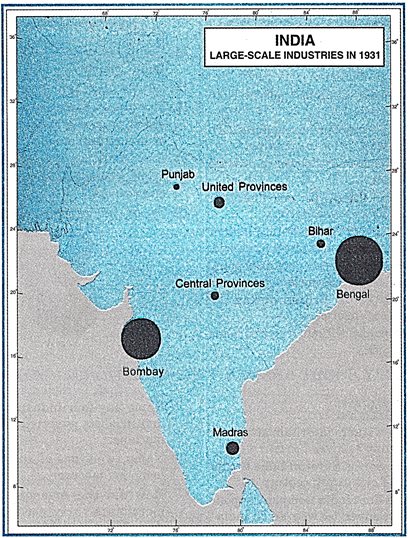 CHAPTER COVERAGE
CHAPTER COVERAGE
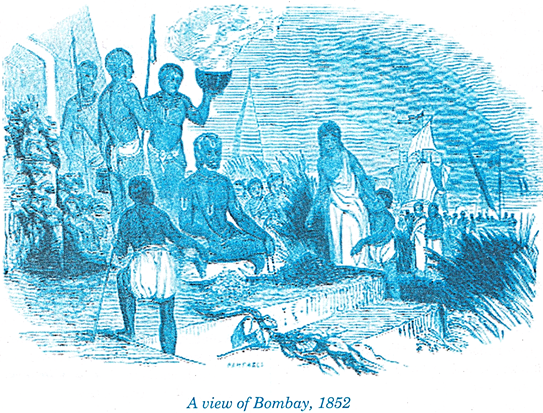
Work, Life and Leisure: Cities in Contemporary World
IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS
Work, Life and Leisure: Cities in Contemporary World
 CHAPTER COVERAGE
CHAPTER COVERAGE
Print Culture and the Modern World
IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |