| <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>Title of page is written here </TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY>The HTML tags that define your page go here </BODY> </HTML> |
 The pattern is +11, +22, +33, + 44
So, 5th term = 44 + 4th term = 44 + 62 =
The pattern is +11, +22, +33, + 44
So, 5th term = 44 + 4th term = 44 + 62 = 
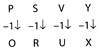
 We placed F for female and M for male above the members.
\[R\div S\Rightarrow R\]is brother of S means R is male
\[\Rightarrow \] R, S, T are siblings
\[Q\times R\Rightarrow Q\]is mother of R means Q is female Q is the mother of R, S, T
\[\text{P}-Q\Rightarrow P\]is father of Q
Clearly, T's mother is Q who is daughter of P.
So, P is maternal grandfather of T.
Hence option (b) is correct.
2. Pointing out to a lady, Rajan said, "She is the daughter of the woman who is the mother of the husband of my mother."
Who is the lady to Rajan?
(a) Aunt (b) Grand-daughter (c) Daughter (d) Sister
Explanation (a):
The relations may be analysed as follows:
Mother's husband - Father; Father's mother - Grandmother; Grandmother's daughter - Father's sister; Father's sister - Aunt.
So, the lady is Rajan's aunt.
We placed F for female and M for male above the members.
\[R\div S\Rightarrow R\]is brother of S means R is male
\[\Rightarrow \] R, S, T are siblings
\[Q\times R\Rightarrow Q\]is mother of R means Q is female Q is the mother of R, S, T
\[\text{P}-Q\Rightarrow P\]is father of Q
Clearly, T's mother is Q who is daughter of P.
So, P is maternal grandfather of T.
Hence option (b) is correct.
2. Pointing out to a lady, Rajan said, "She is the daughter of the woman who is the mother of the husband of my mother."
Who is the lady to Rajan?
(a) Aunt (b) Grand-daughter (c) Daughter (d) Sister
Explanation (a):
The relations may be analysed as follows:
Mother's husband - Father; Father's mother - Grandmother; Grandmother's daughter - Father's sister; Father's sister - Aunt.
So, the lady is Rajan's aunt. | Input : | 45 | 68 | 42 | 12 | 18 | 56 |
| Step I : | 68 | 45 | 42 | 12 | 18 | 56 |
| Step II : | 68 | 56 | 45 | 42 | more...
DIRECTIONS
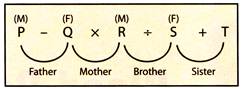
There are eight directions.
These are: East (E), West (W), North (N), South (S), North-East (N-E), North-West (N-W), South-East (S-E), and South-West (S-W)
 The angle between (East and North) or (North and West) or (South and East) or (South and West) is\[90{}^\circ \].
Clockwise : The direction in which the clock moves.
Anticlockwise : The opposite direction of the movement of the hands of a clock.
The angle between (East and North) or (North and West) or (South and East) or (South and West) is\[90{}^\circ \].
Clockwise : The direction in which the clock moves.
Anticlockwise : The opposite direction of the movement of the hands of a clock.
 EXAMPLE
1. A farmer everyday goes to his farm from his home. He walks 400 m towards South. He turns to his left and walks 600 m. He then turns to his right and walks 200 m and reach his farm. How far is the farm from the home and in which direction?
(a) 600\[\sqrt{2}\] m, North-East
(b) 600\[\sqrt{2}\] m, South-East
(c) 800 m, North-East
(d) 800 m, South-East
Explanation (b):
Let the home be at H.
EXAMPLE
1. A farmer everyday goes to his farm from his home. He walks 400 m towards South. He turns to his left and walks 600 m. He then turns to his right and walks 200 m and reach his farm. How far is the farm from the home and in which direction?
(a) 600\[\sqrt{2}\] m, North-East
(b) 600\[\sqrt{2}\] m, South-East
(c) 800 m, North-East
(d) 800 m, South-East
Explanation (b):
Let the home be at H.
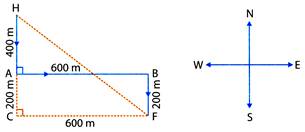 The farmer first walks 400 m from H to A, then A to B 600 m and then B to F 200 m. F be the position of farmer's farm
In \[\Delta HCF,\]
HC = 400 + 200 = 600 m
CF = 600 m
\[\angle HCF=\text{ }90{}^\circ \]
Using Pythagoras theorem,
\[H{{F}^{2}}=H{{C}^{^{2}}}C{{F}^{2}}=2H{{C}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow HF=\sqrt{2\times 600\times 600}=600\sqrt{2}\,\,m\]
Hence farm is \[600\sqrt{2}\,\,m\] away from the home in South-East direction.
2. A rat runs 20' towards East and turns to right, runs 10' and turns to right, runs 9' and again turns to left, runs 5" and then turns to left, runs 12' and finally turns to left and runs 6'. Now, in which direction is the rat facing?
(a) East (b) West (c) North (d) South
Explanation (c):
The farmer first walks 400 m from H to A, then A to B 600 m and then B to F 200 m. F be the position of farmer's farm
In \[\Delta HCF,\]
HC = 400 + 200 = 600 m
CF = 600 m
\[\angle HCF=\text{ }90{}^\circ \]
Using Pythagoras theorem,
\[H{{F}^{2}}=H{{C}^{^{2}}}C{{F}^{2}}=2H{{C}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow HF=\sqrt{2\times 600\times 600}=600\sqrt{2}\,\,m\]
Hence farm is \[600\sqrt{2}\,\,m\] away from the home in South-East direction.
2. A rat runs 20' towards East and turns to right, runs 10' and turns to right, runs 9' and again turns to left, runs 5" and then turns to left, runs 12' and finally turns to left and runs 6'. Now, in which direction is the rat facing?
(a) East (b) West (c) North (d) South
Explanation (c):
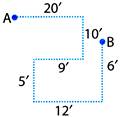 A is initial position & B is final position. Rat is now facing in north direction.
A is initial position & B is final position. Rat is now facing in north direction.
Type-I:
In this section, some groups of geometrical figures are given. A student is required to find which group of the figures show the reasonable relationship among the given classes of items.
EXAMPLE
1. Which one of the diagrams given below represents the relationship among the following three groups of items?
Teachers, Doctors, Children
(a)
 (b) (b)  (c) (c)  (d) (d)  Explanation (c):
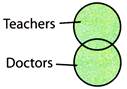
Some teachers may be doctors and some doctors may be teachers.
So teachers and doctors can be represented by two intersecting circles as:
Explanation (c):
Some teachers may be doctors and some doctors may be teachers.
So teachers and doctors can be represented by two intersecting circles as:
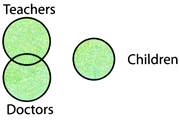
 But the class of children is entirely separate from these two.
So, the final Venn diagram would be as shown below:
But the class of children is entirely separate from these two.
So, the final Venn diagram would be as shown below:
 Type-II:
In this section, a Venn diagram is given, whose each segment (geometrical figure) represents a section of items.
To answer certain questions, a student is required to analyse the diagram carefully.
2. Direction (I - II): The following questions are based on the diagram and information given below:
Triangle represents the married persons
Circle represents unemployed
Square represents men
Rectangle represents vegetarians
Type-II:
In this section, a Venn diagram is given, whose each segment (geometrical figure) represents a section of items.
To answer certain questions, a student is required to analyse the diagram carefully.
2. Direction (I - II): The following questions are based on the diagram and information given below:
Triangle represents the married persons
Circle represents unemployed
Square represents men
Rectangle represents vegetarians
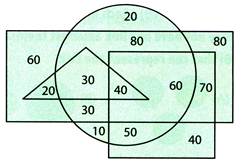 Answer the following questions:
I. How many persons are male vegetarians, who are employed and unmarried?
(a) 70 (b) 40 (c) 120 (d) 180
Explanation (a):
Male vegetarians are in common regions of only square and rectangle. Number of male vegetarians who are employed and unmarried is 70.
II. The number of married men, who are unemployed and vegetarians is
(a) 10 (b) 20 (c) 30 (d) 40
Explanation (d):
The given four characteristics are represented by the common region to all the four geometrical figures. That is 40.
So, the required number of men = 40
Answer the following questions:
I. How many persons are male vegetarians, who are employed and unmarried?
(a) 70 (b) 40 (c) 120 (d) 180
Explanation (a):
Male vegetarians are in common regions of only square and rectangle. Number of male vegetarians who are employed and unmarried is 70.
II. The number of married men, who are unemployed and vegetarians is
(a) 10 (b) 20 (c) 30 (d) 40
Explanation (d):
The given four characteristics are represented by the common region to all the four geometrical figures. That is 40.
So, the required number of men = 40 Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |