The French Revolution
IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS
Nation. People who share a language, culture, customs and history; a group united into a large political, economic and social unit which recognises no law or authority above its own, i.e., it is sovereign in nature.
Nationalism. A feeling of intense loyalty and devotion to one's country.
Revolution. The term means a recognised momentous change in any situation. A revolution can result in the sudden overthrow of an established government or system by force and bloodshed, e.g.. The French Revolution. It can also be a great change that comes slowly and peacefully, e.g., Industrial Revolution.
First Estate. French society was divided into classes called Estates. The First Estate consisted of the Clergy which held vast land, wealth and was exempt from taxation.
Second Estate. It consisted of the aristocracy and controlled all the top positions in the government, parliament and in the army and navy. They were also exempt from taxation and led an extravagant life.
Third Estate. This comprised everyone who was neither nobility nor clergy and constituted 98% of the population. Town dwellers, the wealthy upper middle class (merchants, bankers, doctors, lawyers), lower middle class, craftsmen, shopkeepers and peasants comprised the Third Estate. This class lacked political power, social position and was heavily taxed though there were many differences in their wealth and style of living.
The Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen. In 1789, the French National Assembly adopted a set of basic principles called the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen. Proposed by Lafayette and based on the ideas of Locke, Montesquieu and Jefferson, this document stated that "men are born and remain free and equal in rights" and that the "source of power resides in the people". It guaranteed all Frenchmen the basic rights of liberty, security, equal justice, fair taxes, speech, religion and thought.
Physiocrats. The French economists were called physiocrats. They believed that taxes should be imposed only with the consent of those on whom they are levied. Their beliefs undermined the feudal rights and privileges of the upper classes.
Livre. Unit of currency used in France till 1794.
Clergy. Group of persons invested with special functions in the Church.
Tithe. A tax levied by the Church equal to one-tenth of the agricultural produce.
Taille. Tax paid directly to the state.
Chateau. Castle belonging to a king or nobleman.
Manor. An estate consisting of the Lord's lands and his mansion.
Sceptre. Symbol of royal power.
Negroes. A term used for the indigenous people of Africa, south of the Sahara. A derogatory term not now commonly used.
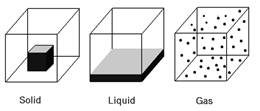 States of Matter
The following are the properties of three states of matter:
Solid
The various properties of solids are:
States of Matter
The following are the properties of three states of matter:
Solid
The various properties of solids are:
 Stone (Solid)
Liquid
The various properties of liquids are:
Stone (Solid)
Liquid
The various properties of liquids are:
 Water (Liquid)
Gas
The various properties of gases are:
Water (Liquid)
Gas
The various properties of gases are:
