 (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d) 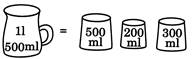 (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d) 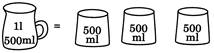 Ans. (d)
1 Litre = 1000ml
1 Litre + 500ml = 1500ml
500ml + 500ml + 500ml = 1500ml = 11 500ml
Ans. (d)
1 Litre = 1000ml
1 Litre + 500ml = 1500ml
500ml + 500ml + 500ml = 1500ml = 11 500ml
Triangle

|
· Triangle has three sides. · It has three vertices. |
Square
|
· Squares have 4 equal sides and 4 right angles. · They have 4 lines of symmetry. · All squares belong to the rectangle family. · All squares belong to the rhombus family. · All squares are also parallelograms. |
Rectangle

|
· Rectangles have 4 sides and 4 right angles.
· They all have 2 lines of symmetry (4 lines if they are also a square)
· All rectangles belong more...
Embedded Figures
OBJECTIVE
· Students will learn to manipulate their mental image of an object in order to reach a certain conclusion.
· They will constitute a noticeable feature of something.
Introduction
Embedded figure is a part of a non-verbal reasoning and it is used to evaluate cognitive skills in children.
Definition
Embedded figure means to find out the hidden figure/shape in a given figure.
Type I: Identify the small part hidden in given figure.
Direction (Examples 1 & 2): In which of the following figures, Figure (X) is exactly embedded as one of its part?
Example - 1
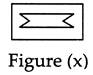 (a)
(a) 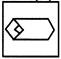 (b) (b)  (c)
(c)  (d) (d)  Ans. (b)
Ans. (b)
 Example - 2
Example - 2
 (a)
(a)  (b) (b)  (c)
(c) 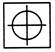 (d) (d) 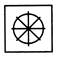 Ans. (c)
Ans. (c)
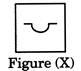
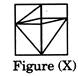
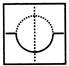 Example - 3
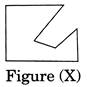
Find out the option figure which contains figure (X) as its part.
Example - 3
Find out the option figure which contains figure (X) as its part.
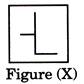 (a)
(a) 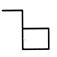 (b) (b)  Ans. (b)
Ans. (b)
 Type II: Identify the figure in which given part is hidden.
Direction (Examples 4 & 5): Select the option figure which is embedded in the given figure (X).
Example 4
Type II: Identify the figure in which given part is hidden.
Direction (Examples 4 & 5): Select the option figure which is embedded in the given figure (X).
Example 4
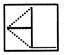
 (a)
(a)  (b) (b)  (c)
(c)  (d) (d)  Ans. (b)
Ans. (b)
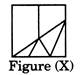
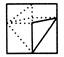 Example 5
Example 5
 (a)
(a)  (b) (b)  (c)
(c)  (d) (d) 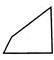 Ans. (d)
Ans. (d)

Mirror Images
OBJECTIVE
· Students will learn how different objects are soon when they get reflected in mirror.
Introduction
The image obtained by putting a mirror in front of the real image is known as mirror image or mirror reflection. The right side of an object appears on the left side and the left side of an object appears on the right side. Phenomenon of
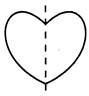
Getting a letter inverted in its mirror image is called the lateral inversion. It is obtained by inverting an object laterally. If we combine the original figure and mirror image together, they form symmetry. Now look at these figures:
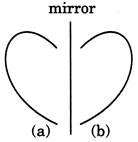 If we combine both the figures (a) and (b), we get a new figure in shape of the heart.
If we combine both the figures (a) and (b), we get a new figure in shape of the heart.
 Mirror Images of Capital Letters
Mirror Images of Capital Letters
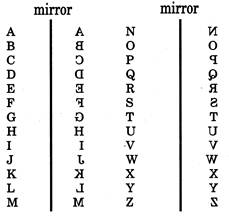 Note- The letters which have the mirror images same as their original form are -
A,H,I,M,0,T,U,V,W,X,Y
Mirror images of small letters
Note- The letters which have the mirror images same as their original form are -
A,H,I,M,0,T,U,V,W,X,Y
Mirror images of small letters
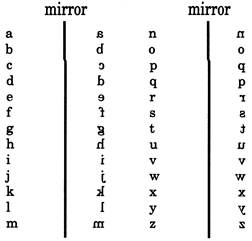 Note- The letters which have the mirror images same as their original form are - i, 1, o, v, w, x
Mirror images of Numbers
Note- The letters which have the mirror images same as their original form are - i, 1, o, v, w, x
Mirror images of Numbers
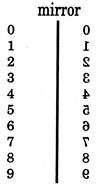 Note- 0 and 8 numbers have the mirror images. Same as their original form.
Types of Mirror Images
Type I: Letter/Number Images
Here, we are given a combination of letters/words/numbers.
We have to find their mirror images out of the given alternatives.
Direction (Examples 1 & 2): In each of the following questions, you are given a combination of alphabets and/ or numbers followed by four alternatives (a), (b), (c), and (d). Choose the alternative which most closely resembles the mirror image of the given combination.
Example - 1
Note- 0 and 8 numbers have the mirror images. Same as their original form.
Types of Mirror Images
Type I: Letter/Number Images
Here, we are given a combination of letters/words/numbers.
We have to find their mirror images out of the given alternatives.
Direction (Examples 1 & 2): In each of the following questions, you are given a combination of alphabets and/ or numbers followed by four alternatives (a), (b), (c), and (d). Choose the alternative which most closely resembles the mirror image of the given combination.
Example - 1
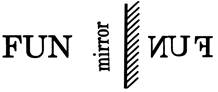 Example - 2
8195
(a)
Example - 2
8195
(a) 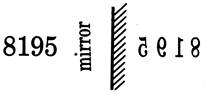 Type II: Geometrical linages
In more...
Type II: Geometrical linages
In more...
Visual Reasoning
OBJECTIVE
 (a)
(a)  Example - 2
Which of the following figure will complete the pattern?
Example - 2
Which of the following figure will complete the pattern?
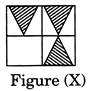 (a)
(a)  (b) (b)  (c)
(c)  (d) (d)  Ans. (c)
Ans. (c)
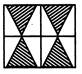 Example - 3
Example - 3
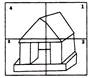
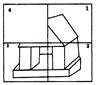 Find out the missing image of the box no. 4.
(a)
Find out the missing image of the box no. 4.
(a)  (b) (b) 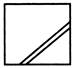 (c)
(c) 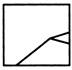 (d) (d) 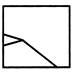 Ans. (c)
Ans. (c)
 Example - 4
Group the given figures into three classes using each figure only once.
Example - 4
Group the given figures into three classes using each figure only once.
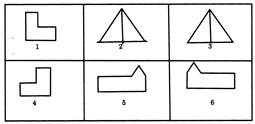 (a) 1, 5; 2, 6; 4, 3 (b) 1, 4; 2, 3; 5, 6
(c) 1, 6; 2, 3; 4, 5 (d) 1, 2; 3, 6; 4, 5
Ans. (b)
Here, figures (I and 4) are similar,
Figures (2 and 3) are similar
and figures (5 and 6) are similar
So, option (b) is correct.
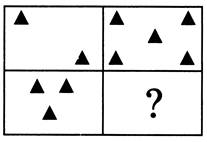
Example - 5
Select a suitable option that would complete the figure matrix.
(a) 1, 5; 2, 6; 4, 3 (b) 1, 4; 2, 3; 5, 6
(c) 1, 6; 2, 3; 4, 5 (d) 1, 2; 3, 6; 4, 5
Ans. (b)
Here, figures (I and 4) are similar,
Figures (2 and 3) are similar
and figures (5 and 6) are similar
So, option (b) is correct.
Example - 5
Select a suitable option that would complete the figure matrix.
 (a)
(a) 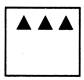 (b) (b)  (c)
(c) 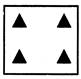 (d) (d)  Ans. (c)
One shaded triangle is increasing in each step.
Ans. (c)
One shaded triangle is increasing in each step.
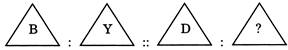
Analogy
Objective
Student will be able to study the similar pattern and completer the given series with the suitable terms.
They will be able to sort to out objects on the basis of similarity
Introduction
It is a similarity or comparability between like features of two things on which a comparison may be based. In these types of questions, a series of numbers or alphabetical letters or combinations of both are given. The students are required to identify the relationship between two or more things and find out the alternative based on that relationship.
Types of Analogy Relationships
Type I: Completing the Analogous Pair
In these types of questions, three words are given and two words are related to each other in some way. The candidates required to find out the relationship between the third and fourth word on the basis of the relationship of the first two words
Picture Based Analogy
Directions (Examples 1 & 2):
There is a certain relationship between the pair of figures given on either side of:: Identify the relationship of given pair and find the missing term.
Example 1
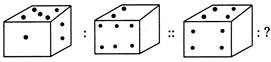 (a)
(a)  (b) (b)  (c)
(c)  (d) (d) 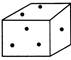 Ans. (a)
Explanation:
Sum of dots on visible face of cube is 8.
Example 2
Ans. (a)
Explanation:
Sum of dots on visible face of cube is 8.
Example 2
 (a)
(a)  (c)
(c)  (d) (d)  Ans. (b)
Explanation:
First figure of the pair can be put in the second figure.
Type II: Number Based Analogy
Direction (Example 3): Two numbers written in the arrow are related to each other. Find the missing term in the second arrow following the same rule.
Example 3
Ans. (b)
Explanation:
First figure of the pair can be put in the second figure.
Type II: Number Based Analogy
Direction (Example 3): Two numbers written in the arrow are related to each other. Find the missing term in the second arrow following the same rule.
Example 3
 (a) Z (b) Y
(c) V (d) W
Ans. (d)
Explanation:
As, 'B' is second letter from the starting in the English alphabet and 'Y' is second letter from the end. Similarly, 'D' is fourth letter from the starting and 'W more...
(a) Z (b) Y
(c) V (d) W
Ans. (d)
Explanation:
As, 'B' is second letter from the starting in the English alphabet and 'Y' is second letter from the end. Similarly, 'D' is fourth letter from the starting and 'W more...
Patterns
OBJECTIVE
 Pattern 1 Pattern 2 Patterns 3
(a) 10 (b) 12
(c) 15 (d) 16
Ans. (c)
Explanation:
Smiling faces in pattern 1=3
Smiling faces in pattern 2=6
Smiling faces in pattern 3=9
So, the Pattern is as follows
Pattern 1 Pattern 2 Patterns 3
(a) 10 (b) 12
(c) 15 (d) 16
Ans. (c)
Explanation:
Smiling faces in pattern 1=3
Smiling faces in pattern 2=6
Smiling faces in pattern 3=9
So, the Pattern is as follows
 (a)
(a) 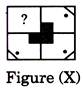 (a)
(a) 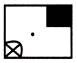 (b) (b) 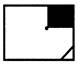 (c)
(c) 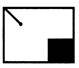 (d) (d) 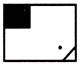 Ans (d)
Ans (d)
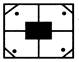 Type II: Number Based Pattern
Example - 4
Complete the more...
Type II: Number Based Pattern
Example - 4
Complete the more...
Type I:
How to find the missing term or next term in (number or letter or figure) series to continue the given series?
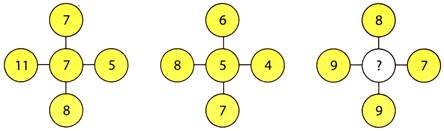 (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5
Explanation (b):
First we carefully study the two given complete patterns.
In the first pattern, the middle term is the sum of difference between the top and bottom number & left and right number.
\[(11-5)+(8-7)=6+1=7\]
Similarly, in second pattern \[(8-4)+7-6)=4+1=5\]
Hence, in third pattern the missing number is \[(9-7)+(9-8)=2+1=3\].
2. Find the missing number in the series below:
3, 6, 11, 18, 27____?____, 51,_____?____
(a) 30, 55 (b) 34, 60 (c) 38, 66 (d) 42, 71
Explanation (c):
Rule followed in the series is:
Difference between consecutive terms are consecutive odd numbers.
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5
Explanation (b):
First we carefully study the two given complete patterns.
In the first pattern, the middle term is the sum of difference between the top and bottom number & left and right number.
\[(11-5)+(8-7)=6+1=7\]
Similarly, in second pattern \[(8-4)+7-6)=4+1=5\]
Hence, in third pattern the missing number is \[(9-7)+(9-8)=2+1=3\].
2. Find the missing number in the series below:
3, 6, 11, 18, 27____?____, 51,_____?____
(a) 30, 55 (b) 34, 60 (c) 38, 66 (d) 42, 71
Explanation (c):
Rule followed in the series is:
Difference between consecutive terms are consecutive odd numbers.
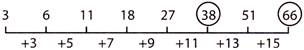
In this topic, two pair of figures is given on either side of:
There is a certain relationship between each pair.
The student has to identify the relation and find the missing figure.
CLASSIFICATION
How to classify or find the odd figure/different figure/similar figure amongst the others?
Observe the figures in questions on the basis of their shapes, size, shadings, their parts, their mirror images, number of sides, curved an straight characteristics etc., to find the odd figure, different figure or similar figure amongst the given figures.
EXAMPLE
1. Which of the following options is different from others?
(a)
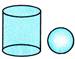 (b) (b) 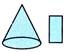 Explanation (d):
In options A, B & C pair or figure are related to each other as corresponding shape can be made from the solid figure.
2. There is a certain relationship between the pair of figures given on either on either side of :: identify the relationship of given pair and find the missing term.
Explanation (d):
In options A, B & C pair or figure are related to each other as corresponding shape can be made from the solid figure.
2. There is a certain relationship between the pair of figures given on either on either side of :: identify the relationship of given pair and find the missing term.
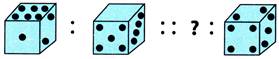 (a)
(a)  (b) (b)  (c) (c)  (d) (d)  Explanation (a):
Number of dots on visible faces of cubes is 9.
Explanation (a):
Number of dots on visible faces of cubes is 9.
Type I:
How to arrange the numbers given to the corresponding letter so that they form a meaningful word?
Arrange the letters in the different combinations given in options to find meaningful word.
Type II:
Finding the word from the options that can/cannot be formed from the given letters.
Students have to observe carefully all the letters given in the question and find the combination of letters from the given options that contains or does not contains letters.
Type III:
How to form a meaningful word and find the category of word?
Arrange the given jumbled letters in meaningful word and identify the category in which formed word lies.
Type IV:
How to identify the combination of letters that has same number of skipped letters between the adjacent letters?
Write the alphabetical series in order, then observe carefully all the options.
EXAMPLE
1. From a meaningful word by arranging given numbers corresponding to the letters given below.
S E W N
(a) 2, 1, 3, 4 (b) 2, 3, 4, 1
(c) 4, 2, 3, 1 (d) 2, 3, 1, 4
Explanation (c):
From (a): 2 1 3 4 = E S W N
From (b): 2 3 4 1= E W N S
From (c): 4 2 3 1 = N E W S
From (d): 2 3 1 4 = E W S N
Only in option (c), a meaningful word is formed.
2. From a meaningful word from given jumbled letters and find its category.
(a) colour (b) Fruit
(c) vegetable (d) shape
Explanation (a): Word formed from CLKBA is BLACK which is a name of colour.
more...
Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |