| Word | Synonyms | ||||||||
| Aid | Help, relief, support | ||||||||
| Brave | Courageous, intrepid, impudent | ||||||||
| Clever | Able, skillful, intelligent | ||||||||
| Courage | Boldness, valour, bravery | ||||||||
| Deliver | Relieve, rescue, discharge | ||||||||
| Destroy | Demolish, ruin, raze | ||||||||
| Dull | Stupid, blunt, boring | ||||||||
| Ecstasy | Joy, bliss, enthusiasm | ||||||||
| Gift. | Present, donation, contribution | ||||||||
| Ideal | more...
Use of Possessives
When a noun shows possession, it is said to be in the possessive case.
For example:
Story Construction
The process of step-wise arrangement of the ideas, acts and occurrences which gives us some moral or idea is called a story. The main parts of a story are:
(i) Heading
(ii) Plot
(iii) Moral
Some stories are given below:
Story - 1: Unity is Strength
A poor farmer had four sons. They did not help their father in the field. They always quarrelled among themselves. The farmer was unhappy. He tried to set them right, but in vain.
The farmer was always sad. He fell ill. His end was near. He wanted to unite his sons. He thought of a plan. He called his sons. He gave them a bundle of sticks. He asked them to break it. Each tried to break the bundle but failed.
The father then untied the bundle. The sons broke the sticks easily. At this the father said, "Be united like the bundle. If you are united none will harm you." The sons learnt a lesson. They never quarrelled again.
Moral: United we stand, divided we fall.
Story - 2: The Hidden Treasure
There was an old farmer. He had four lazy sons. Before dying he wanted to teach his sons the value of hard work. He called his sons to his bed-side. He said, "Dear sons, long ago my father gave me a box full of gold coins. For fear of robbers, I buried it in the fields. I want you to dig it out after my death and lead a happy life."
After a few days, the farmer passed away. The sons went to fields with spades and pick- axes. They dug every inch of the ground. But no treasure was found. A passerby asked them to sow wheat. The sons did so. They reaped a rich harvest that year. They realized that the real treasure was in hard work. This was what their father wanted to teach them.
Moral: Hard work is the real treasure.
Story - 3: Two Friends and the Bear
Mohan and Sohan were friends. They lived in a village. Mohan was true and loyal but Sohan was selfish.
One day they set out on a long journey their way lay through a thick forest. As they were passing through it, they saw a bear. It was coming towards them. Sohan at once climbed up a nearby tree. He was now safe. Mohan did not know how to climb a tree. But he did not lose his presence of mind. He had heard that the bear did not eat the dead.
So he lay down on the ground and held his breath.
The bear came. It sniffed Mohan and took him for a dead man. So it went away. Now Sohan got down the tree. He said to Mohan, "What did the bear say in your ear?" Mohan replied, "The bear advised me not to more...
Short Paragraph Construction
Paragraph: Paragraph is a small unit of composition. It is a group of sentences which describes only one theme.
Some paragraphs are given below:
My Mother
It is very well said in Vedas that "A mother holds the same place as God". She is the symbol of kindness. She loves her child selflessly. She is the first teacher. She shapes the overall personality of the child. My mother is the most precious gift that God has given me. Whenever 1 return from school her sweetest greeting helps me forget all the problems I had to face throughout the day. She takes care of my smallest requirements. She teaches me to face all types of challenges of lite. I cannot imagine my world without my mother.
My school
My school is situated very near to my house. It is a very big school. It is red in colour. It has a big ground play where we play games. It has 3 science laboratories, 2 computer practical rooms and a big library. The library houses have many informative books. Apart from this my school has a big auditorium. Generally, all the school functions are held in this auditorium. My school has lots of open spaces and it is always busting with life. I love my school very much.
Number Sense and Numeration
Introduction
Everything is counted by numbers. Numbers are the symbolic representation of counted objects. Categorized of numbers are basically dependent on their factors and divisibility.
Types of Number
Natural Numbers
Counting numbers are known as natural numbers.
For example, natural numbers (N) = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ?.. infinite}
Whole Numbers
Counting numbers including 0 are known as whole numbers.
For example, whole numbers (W) = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4?. infinite}
Prime Numbers
Those numbers having two factors 1 and the number itself are called prime numbers.
For example, prime numbers (P) = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13 etc.}
Twin Numbers
Two numbers with difference of 2 are called twin primes.
For example: {3, 5}, {5, 7}, {11, 13} etc.
Note:
2 is even prime number.
Composite Numbers
Numbers having more than two factors, 1 and the number itself, are called composite numbers.
For example: {4, 6, 8, 9, 10 etc.}
Even Number
more...
Addition and Subtraction
Addition
Addition is the combination of two or more quantities in a single quantity. This is one of the four basic arithmetic operations. Symbol for addition is +.
Addition of Four Digits Numbers without Carry Over
Following are the steps used in this type of addition.
For example: addition of 4784 and 3214.
Step 1: Add ones 4 + 4 = 8. Write 8 under ones column.
Step 2: Add tens 8 + 1 = 9. Write 9 under tens column.
Step 3: Add hundreds 7 + 2 = 9. Write 9 under hundreds column.
Step 4: Add thousands 4 + 3 = 7. Write 7 under thousands column.
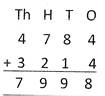 Hence, addition of 4784 + 3214 = 7998.
Addition of Four Digit Numbers with Carry Over
Following are the steps used in this type of addition.
For example addition of 7569 and 5984.
Step 1: Add ones, 9 + 4 = 13 = 1 tens + 3 ones. Write 3 under ones column and carry one tens to the tens column.
Step 2: Add tens, 6 + 8 + 1 (carry over) = 15 tens = 1 hundred + 5 tens.
Write 5 under tens column and carry 1 hundred to the hundreds column.
Step 3: 1 thousand 5+9+1 (carry over) =15 hundreds.
Write 5 under hundreds column and carry 1 thousand to the thousand column
Step more...
Hence, addition of 4784 + 3214 = 7998.
Addition of Four Digit Numbers with Carry Over
Following are the steps used in this type of addition.
For example addition of 7569 and 5984.
Step 1: Add ones, 9 + 4 = 13 = 1 tens + 3 ones. Write 3 under ones column and carry one tens to the tens column.
Step 2: Add tens, 6 + 8 + 1 (carry over) = 15 tens = 1 hundred + 5 tens.
Write 5 under tens column and carry 1 hundred to the hundreds column.
Step 3: 1 thousand 5+9+1 (carry over) =15 hundreds.
Write 5 under hundreds column and carry 1 thousand to the thousand column
Step more...
Multiplication and Division
Multiplication
Multiplication means repeated addition. The symbol for the notation of multiplication is '
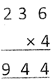 Multiplication of Four Digit Numbers with Two Digit Numbers
Following are the steps for multiplication of four digit numbers with two digit numbers:
For example, 4526
Multiplication of Four Digit Numbers with Two Digit Numbers
Following are the steps for multiplication of four digit numbers with two digit numbers:
For example, 4526
Fraction
Introduction
The Latin name of fraction is fractus. It means broken. Fractions are always in ratio form. It has two parts, upper and lower part. The upper part is called numerator and lower part is denominator.
Fractions in its Lowest Term
The lowest term of a fraction is obtained by dividing numerator and denominator with common divisor. The lowest form of the fraction \[\frac{6}{9}\,\,is\,\frac{2}{3}\] . The lowest term of the fraction \[\frac{6}{9}\] is obtained by dividing the numerator and denominator with a common divisor 3.
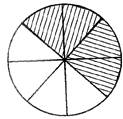 (a) \[\frac{3}{8}\] (b) \[\frac{1}{2}\]
(c) \[\frac{1}{5}\] (d) All the above
(e) None of these
Ans. (b)
more...
(a) \[\frac{3}{8}\] (b) \[\frac{1}{2}\]
(c) \[\frac{1}{5}\] (d) All the above
(e) None of these
Ans. (b)
more... Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |