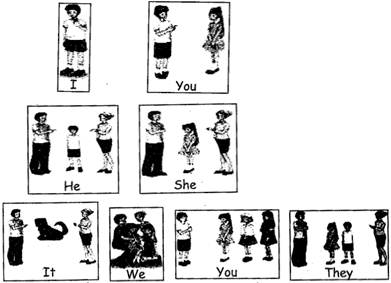
 TYPES OF PRPONOUN
(a) Personal pronoun:
TYPES OF PRPONOUN
(a) Personal pronoun:
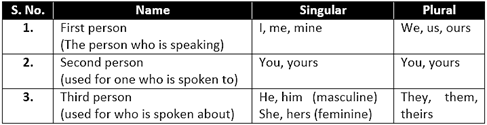 Remember
Use a pronoun instead of noun.
The pronoun you use must follow its noun in number and gender. Example:
Ram is going to market. He has to get mangoes.
(b) Reflexive pronouns: When we add 'self' or ?selves? personal pronoun they become Reflexive pronouns. 'Self' is added to 'my, your, her and him' and 'selves' to our, your and them'.
Example: You must do your homework yourself. They went together themselves.
(c) Demonstrative pronouns: These point to the object they belong to. Example:
This is a book.
That is a calendar.
These are books.
Those are calendars.
Remember
Use a pronoun instead of noun.
The pronoun you use must follow its noun in number and gender. Example:
Ram is going to market. He has to get mangoes.
(b) Reflexive pronouns: When we add 'self' or ?selves? personal pronoun they become Reflexive pronouns. 'Self' is added to 'my, your, her and him' and 'selves' to our, your and them'.
Example: You must do your homework yourself. They went together themselves.
(c) Demonstrative pronouns: These point to the object they belong to. Example:
This is a book.
That is a calendar.
These are books.
Those are calendars.
 Poem
I am hungry.
You are hungry.
He is hungry.
She is hungry.
We are hungry.
They are hungry.
Everybody is hungry.
I am thirsty.
You are thirsty.
He is thirsty.
She is thirsty.
We are thirsty.
They are thirsty.
Everybody is thirsty.
I am happy
You are happy.
He is happy.
She is happy.
We are happy.
They are happy.
Everybody is happy.
(d) Interrogative pronouns: To ask questions, the words who, what which, whose, whom' are used/All of them are Interrogative Pronouns. It is used to begin a question, "who, whom, whose' are used for persons, which' is used for persons as well as things. 'What' is used only for things.
Examples:
Who are you?
What is your name?
Which is your book?
Whom does this glass belong to?
The other way to classify pronouns is:
Poem
I am hungry.
You are hungry.
He is hungry.
She is hungry.
We are hungry.
They are hungry.
Everybody is hungry.
I am thirsty.
You are thirsty.
He is thirsty.
She is thirsty.
We are thirsty.
They are thirsty.
Everybody is thirsty.
I am happy
You are happy.
He is happy.
She is happy.
We are happy.
They are happy.
Everybody is happy.
(d) Interrogative pronouns: To ask questions, the words who, what which, whose, whom' are used/All of them are Interrogative Pronouns. It is used to begin a question, "who, whom, whose' are used for persons, which' is used for persons as well as things. 'What' is used only for things.
Examples:
Who are you?
What is your name?
Which is your book?
Whom does this glass belong to?
The other way to classify pronouns is:
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:
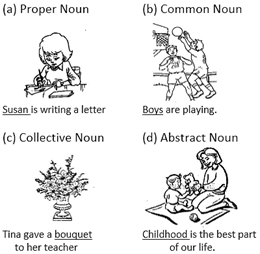
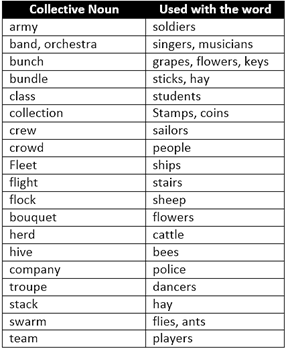 FORMATION OF ABSTRACT NOUNS
FORMATION OF ABSTRACT NOUNS
 Activity
Create a collage of nouns. Get a large piece of poster board and using a marker, make one heading for common nouns, proper noun and collective nouns. Clip them out and paste or tape them underneath the proper heading. This collage will help you visualize the use of the three nouns.
Important Tip
An abstract noun relates to something which cannot actually be perceived by the senses. It denotes quality like cleverness, kindness, state like poverty, youth, action like laughter, movement etc. abstract nouns should not be confused with verbs because verbs are action or doing words which can be seen when they are done like writing, running, eating etc.
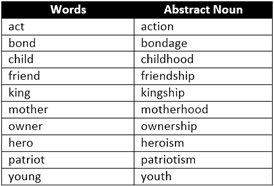
ONE WORD SUBSTITUTION
There are words which can replace a group or words. Such nouns enhance the vocabulary and are helpful in explaining thoughts. There are many more words. A few words have been mentioned here for you better understanding.
Activity
Create a collage of nouns. Get a large piece of poster board and using a marker, make one heading for common nouns, proper noun and collective nouns. Clip them out and paste or tape them underneath the proper heading. This collage will help you visualize the use of the three nouns.
Important Tip
An abstract noun relates to something which cannot actually be perceived by the senses. It denotes quality like cleverness, kindness, state like poverty, youth, action like laughter, movement etc. abstract nouns should not be confused with verbs because verbs are action or doing words which can be seen when they are done like writing, running, eating etc.
ONE WORD SUBSTITUTION
There are words which can replace a group or words. Such nouns enhance the vocabulary and are helpful in explaining thoughts. There are many more words. A few words have been mentioned here for you better understanding.
 (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  (e)
(e) 
| No. | Subject | Predicate |
| a. | The sun | rises in the east |
| b. | The Queen of England | more...
Real Life Example
As electronic communication technologies such as e mail and text messaging have become more and more prevalent, letter writing still remains an important skills to discover. In fact e-mail writing is also a kind of letter writing.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:-
Historical Preview
"Bury the hatchet."
Native Americans used to bury weapons to show that fighting had ended and enemies were now at peace. Today, the idiom means to make up with a friend after an argument or fight.
"Raining cats and dogs."
In Norse mythology, the dog is associated with wind and the cat with storms. This expression means it?s raining very heavily.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:-
understand what idioms, phrases and proverbs mean.
apply them in writing.
understand their importance in day to day communication
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
Idioms
Idiom is an expression of two or rnore words that means something other than the literal meanings of its individual words. Idioms are used to replace a literal word or expression. Definition: An idiom is a phrase where the words together have a meaning that is different from the dictionary definitions of the individual words.
For example:
He cried crocodile tears because he wanted his dad to buy him something. Just as a crocodile cannot cry, the boy was not crying at all! He was just acting! People use idioms to make their language richer and more colourful. Idioms and idiomatic expressions can be more precise than the literal words, often using fewer words but saying more.
Phrases
A phrase is a group of words that have a particular meaning when used together, or which someone uses on a particular occasion.
Example:
He disposed off his car for a small sum. Here the phrase 'disposed off can easily be replaced with "sold", so, that's how we use a
PROBERBS
A short well-known statement that gives advice or expresses something that is generally true. Take the famous proverb: Slow and steady wins the race. 'A penny saved is a penny earned' is another example of a proverb.
AN INTERESTING FACT
Every proverb has a story behind it.
Here's a story about the Hare and the Tortoise:
STORY
Once upon a time, there were two good friends the hare and the tortoise. One day the hare told the tortoise "tortoise are too slow, I can run much faster than you.? The tortoise replied, fine! Let's run a race. We'll see who wins it. On a fixed date and time, they ran the race. The hare was so confident that he started taking short naps in between the race. The tortoise plodded along. After he had slept for the third time, the hare opened his eyes to see that the tortoise had won the race.
Lesson: Slow and steady wins the race.
TIP
The best way to remember this proverb is to remember the story associated with it.
Amazing Fact
To "shed crocodile tears."
Crocodiles have a reflex that causes their eyes to tear when they open their mouths. This makes it look as though they are crying while devouring their prey. In fact, neither crocodiles nor people who shed "crocodile" tears feel sory for their actions.
Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |