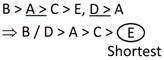 Rest of the options is incorrect because of the correctness of option (c).
Rest of the options is incorrect because of the correctness of option (c).
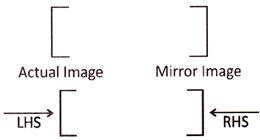 Mirror Image of Capital Letters and Numbers (1 to 9):
Mirror Image of Capital Letters and Numbers (1 to 9):
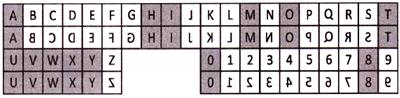 Example-1
1. Choose the option which most resembles the mirror image of the given combination.
Example-1
1. Choose the option which most resembles the mirror image of the given combination.
 more...
more...  So, we have, \[\frac{1}{5}+\frac{3}{5}=\frac{1+3}{5}=\frac{4}{5}\]
Therefore, the sum of like fractions \[=\frac{Sum\text{ }of\text{ }Numerators}{Common\text{ }Denominator}\]
Word Problems Based on Fractions
A fraction is defined as a portion of the whole. It is made up of two numbers: Numerator and Denominator. Fraction is a small amount of whole quantity. For example, if a piece of wire is divided into three parts, then each part is one-third part or \[\frac{1}{3}\] part of whole. The word problems involving fractions are usually based on real-life. Let us look at the following problems based on fractions.
Time and Clock
Time is important to plan our day. Time is the ongoing sequence of events. We use time to order events in the past, present and future. Time is passing non-stop. We use a clock or watch to measure time. Time is measured in seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years with the help of clocks and calendars.
Indian Currency
Currency is a generally accepted form of money, including coins and paper notes. Different countries uses different currencies. Indian currency is know as Rupees. Symbol for Indian rupees is ‘Rs.’ and Symbol for Indian paise is 'p'. We write 78 rupees as Rs.78 and 50 paise as 50 p. There are 100 paise in one rupee. Suppose we have rupees one hundred four and more...
So, we have, \[\frac{1}{5}+\frac{3}{5}=\frac{1+3}{5}=\frac{4}{5}\]
Therefore, the sum of like fractions \[=\frac{Sum\text{ }of\text{ }Numerators}{Common\text{ }Denominator}\]
Word Problems Based on Fractions
A fraction is defined as a portion of the whole. It is made up of two numbers: Numerator and Denominator. Fraction is a small amount of whole quantity. For example, if a piece of wire is divided into three parts, then each part is one-third part or \[\frac{1}{3}\] part of whole. The word problems involving fractions are usually based on real-life. Let us look at the following problems based on fractions.
Time and Clock
Time is important to plan our day. Time is the ongoing sequence of events. We use time to order events in the past, present and future. Time is passing non-stop. We use a clock or watch to measure time. Time is measured in seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years with the help of clocks and calendars.
Indian Currency
Currency is a generally accepted form of money, including coins and paper notes. Different countries uses different currencies. Indian currency is know as Rupees. Symbol for Indian rupees is ‘Rs.’ and Symbol for Indian paise is 'p'. We write 78 rupees as Rs.78 and 50 paise as 50 p. There are 100 paise in one rupee. Suppose we have rupees one hundred four and more... | Plane Shape | Solid Shape |
| (a) they are two dimension (2D) shape | (a) they are three dimension (3D) shape |
| (b) They are only length and breadth but no thickness | (b) They have length breadth but no thickness |
| (c) They have only one face | (c) They have many face |
| (d) They do not occupy volume. | (d) They occupy volume. |
|
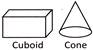
(e) For example:
|
e) For example:
 |
| SI units or Base Units | |
| Physical Qualities | SI Unit |
| Length | Metre (m) |
| Mass | Kilometre (kg) |
| Time | Second (s) |
| Red |
|
| Blue |
|
| Green |
|
| Yellow |
|
| White |
 more... more...
Me and My Family
Interesting Facts
 Ria, who is Kiara's friend, has a big nuclear family because she lives with her two brothers and parents.
Ria, who is Kiara's friend, has a big nuclear family because she lives with her two brothers and parents.
 Joint family: A family in which grandparents, parents, uncles, aunts and cousins live together in the same house is called as a joint family.
Joint family: A family in which grandparents, parents, uncles, aunts and cousins live together in the same house is called as a joint family.
 Do you know?
Do you know?
 more...
more...
Our Surroundings
Interesting Fact
 2. Architect: They drew up the blueprints for the buildings.
2. Architect: They drew up the blueprints for the buildings.
 3. Chef: The chef prepared a marvelous four course meal.
3. Chef: The chef prepared a marvelous four course meal.
 4. Electrician: We need to call an electrician to come and fix the wiring.
4. Electrician: We need to call an electrician to come and fix the wiring.
 5. Farmer: The farmer sold his vegetables at the local farmer's market.
5. Farmer: The farmer sold his vegetables at the local farmer's market.
 6. Judge: Judge make serious decisions when sentencing criminals who are found guilty.
6. Judge: Judge make serious decisions when sentencing criminals who are found guilty.
 7. Doctor: A doctor treat the patients when they fall ill.
7. Doctor: A doctor treat the patients when they fall ill.
 8. Nurse: Nurses make sure patients needs are taken care of in hospitals.
8. Nurse: Nurses make sure patients needs are taken care of in hospitals.
 9. Pilot; A pilot flew the airplane.
9. Pilot; A pilot flew the airplane.
 10. Builders: The builder finished the home in record time.
10. Builders: The builder finished the home in record time.
 PLACES OF WORSHIP
1. Church: Christians pray to God in church. They pray to Jesus Christ and the Bible is their holy book. A Christian prayer is called a service and their priest is called a clergyman.
PLACES OF WORSHIP
1. Church: Christians pray to God in church. They pray to Jesus Christ and the Bible is their holy book. A Christian prayer is called a service and their priest is called a clergyman.
 2. more...
2. more...
Our Body
Interesting Facts
|