 Everything around us is made of curved lines or straight lines or a combination of both lines.
SHAPES AND SOLIDS
All things around us have shapes. There are 2 types of shapes:-
Flat Shape
Solid Shape
Real Life Examples
Line and shapes are useful in architecture and carpentry.
We see different shapes all around us.
Eg: football, book, pencil
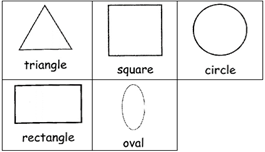
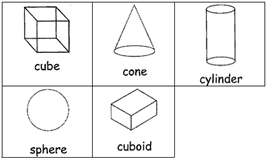
Square, circle, triangle and rectangle are flat shapes. Sphere, cone, cylinder, cube and cuboid are solid shapes.
FLAT SHAPES
Everything around us is made of curved lines or straight lines or a combination of both lines.
SHAPES AND SOLIDS
All things around us have shapes. There are 2 types of shapes:-
Flat Shape
Solid Shape
Real Life Examples
Line and shapes are useful in architecture and carpentry.
We see different shapes all around us.
Eg: football, book, pencil
Square, circle, triangle and rectangle are flat shapes. Sphere, cone, cylinder, cube and cuboid are solid shapes.
FLAT SHAPES
 SOLID SHAPES
SOLID SHAPES
 FLAT SHAPES
Squares, triangles, rectangles, circles, and lines can be drawn on a piece of paper.
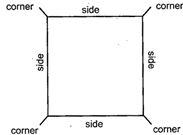
Most of them have sides and corners but circle has neither side nor corner.
1. SQUARE
Square has four sides and four corners.
FLAT SHAPES
Squares, triangles, rectangles, circles, and lines can be drawn on a piece of paper.
Most of them have sides and corners but circle has neither side nor corner.
1. SQUARE
Square has four sides and four corners.
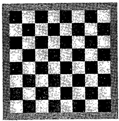 E.g. Chess board.
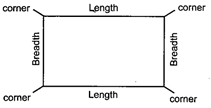
2. RECTANGLE
A rectangle has four sides and four corners.
The longer side is called length.
The shorter side is called breadth.
E.g. Chess board.
2. RECTANGLE
A rectangle has four sides and four corners.
The longer side is called length.
The shorter side is called breadth.
 E.g. Door.
3. TRIANGLE
E.g. Door.
3. TRIANGLE
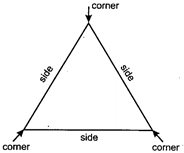 A triangle has three sides and three corners.
A triangle has three sides and three corners.
 E.g. A pizza slice.
4. CIRCLE:
E.g. A pizza slice.
4. CIRCLE:
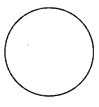 A circle is round and has no side.
A circle is round and has no side.
 E.g. A circular plate.
5. OVAL
E.g. A circular plate.
5. OVAL
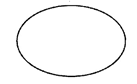 An oval has no sides.
An oval has no sides.
 E.g. An egg.
We will study about solid shapes in the next class.
ROLLING AND SLIDING
Have you noticed that some objects roll while some slide?
E.g. An egg.
We will study about solid shapes in the next class.
ROLLING AND SLIDING
Have you noticed that some objects roll while some slide?
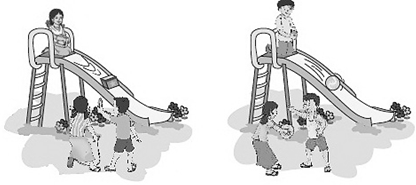 When we push round objects like ball, etc., they roll. When we push flat objects like book, dice etc., they slide. Do you know the reason?
This is because a ball has a curved or round surface that is why a ball rolls.
A dice has flat surface that is why a dice slides.
Observe different objects at your home or school and try to identify their shapes. Discuss your observations with your family, friends and more...
When we push round objects like ball, etc., they roll. When we push flat objects like book, dice etc., they slide. Do you know the reason?
This is because a ball has a curved or round surface that is why a ball rolls.
A dice has flat surface that is why a dice slides.
Observe different objects at your home or school and try to identify their shapes. Discuss your observations with your family, friends and more... 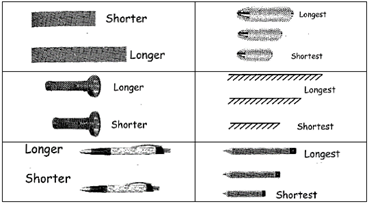 Compare Height: Taller or Shorter
Height tells us how tall or short something is.
We use words ‘taller’ and ‘shorter’ to compare the height of things that are standing up
We can compare the height of different things by making them stand next to each other.
Compare Height: Taller or Shorter
Height tells us how tall or short something is.
We use words ‘taller’ and ‘shorter’ to compare the height of things that are standing up
We can compare the height of different things by making them stand next to each other.

 Historical Preview
In ancient times, there was no measuring system. People used to measure things with the help of body parts. For example: to measure the length of a cloth they used the handspans.
Standard Units
Standard units of measurement of
(a) Length:
Centimetre (for small lengths)
Metre (for big lengths)
(b) Capacity: Litre (for more capacity)
Millilitre (for less capacity)
(c) Weight: kg (for Heavy object) g (for light objects)
MEASURING LENGTHS
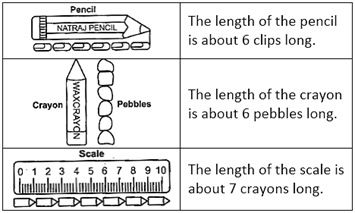
1. Using Another Object
We can measure the length of an object by using another object.
For Examples:
Historical Preview
In ancient times, there was no measuring system. People used to measure things with the help of body parts. For example: to measure the length of a cloth they used the handspans.
Standard Units
Standard units of measurement of
(a) Length:
Centimetre (for small lengths)
Metre (for big lengths)
(b) Capacity: Litre (for more capacity)
Millilitre (for less capacity)
(c) Weight: kg (for Heavy object) g (for light objects)
MEASURING LENGTHS
1. Using Another Object
We can measure the length of an object by using another object.
For Examples:
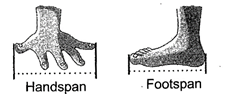
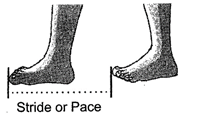
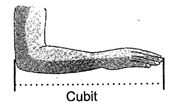
 2. Using Body Parts:
We can measure the length of an object by using body parts. For example, you can use you hand to measure length of you study table.
Non- standard Units of Measuring Length
2. Using Body Parts:
We can measure the length of an object by using body parts. For example, you can use you hand to measure length of you study table.
Non- standard Units of Measuring Length
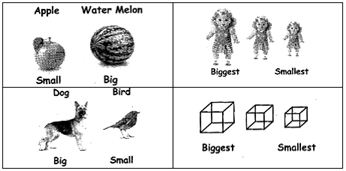
 COMPARING SIZE
The words big and small tell us about the size of an object.
For examples:
COMPARING SIZE
The words big and small tell us about the size of an object.
For examples:
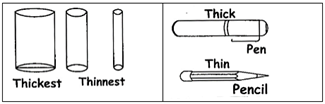
 COMPARING THICKNESS
The words thick and thin tell us about the thickness of an object.
For examples:
COMPARING THICKNESS
The words thick and thin tell us about the thickness of an object.
For examples:
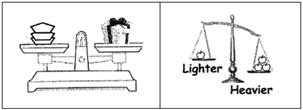
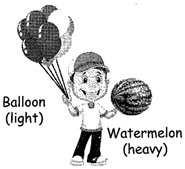
 WEIGHT
A measurement of how heavy something is.
We use the words 'heavier' or 'lighter' to compare the weights of things.
WEIGHT
A measurement of how heavy something is.
We use the words 'heavier' or 'lighter' to compare the weights of things.
 more...
more... 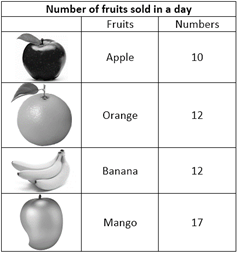 Do you know?
Data handling represents data in the form of pictures (called pictograph). These pictographs used by various news channels to display weather report on news.
Real life example:
Data Handling is widely used in collection of scores of students in various exams.
Data handling helps the doctors to keep records of their patients.
Once we have information data, the next step is to get result from it.
The information we get from the above data is that Mangoes are sold the most. Apples are sold the least.
SORT AND ORGANISE
Do you know?
Data handling represents data in the form of pictures (called pictograph). These pictographs used by various news channels to display weather report on news.
Real life example:
Data Handling is widely used in collection of scores of students in various exams.
Data handling helps the doctors to keep records of their patients.
Once we have information data, the next step is to get result from it.
The information we get from the above data is that Mangoes are sold the most. Apples are sold the least.
SORT AND ORGANISE

 Look at the picture of two rooms, room A and room B.
Which room looks neat and clean?
Room B looks neat and clean as things are properly organised in Room B.
Let us understand how to sort and organise things.
Sorting: Grouping objects on the basis of common features is called Sorting'.
Organising: Arranging objects in a proper or systematic manner is called organising.
An organised room or display looks neat and clean. For example room B in above example.
Ramu has opened a new stationery shop. It has pens, pencils, erasers, books, notepads, envelopes, coloured chalks, papers and stickers at one place. How can he neatly arrange everything?
He can sort things and organise them on the basis of their size, shape, colour etc.
We can make a table to help us to sort our things.
Annie and her friends wants to celebrate Christmas. They want to purchase some items to decorate their Christmas tree. They prepare a list of various items, which are required to decorate the tree. The table given below shows the list of items and the number of items. This list will help Annie and her friends to remember the items to be purchased and their numbers.
.
Look at the picture of two rooms, room A and room B.
Which room looks neat and clean?
Room B looks neat and clean as things are properly organised in Room B.
Let us understand how to sort and organise things.
Sorting: Grouping objects on the basis of common features is called Sorting'.
Organising: Arranging objects in a proper or systematic manner is called organising.
An organised room or display looks neat and clean. For example room B in above example.
Ramu has opened a new stationery shop. It has pens, pencils, erasers, books, notepads, envelopes, coloured chalks, papers and stickers at one place. How can he neatly arrange everything?
He can sort things and organise them on the basis of their size, shape, colour etc.
We can make a table to help us to sort our things.
Annie and her friends wants to celebrate Christmas. They want to purchase some items to decorate their Christmas tree. They prepare a list of various items, which are required to decorate the tree. The table given below shows the list of items and the number of items. This list will help Annie and her friends to remember the items to be purchased and their numbers.
.  PRESENTING DATA
We can present data in the form of table, pictures, graph, bar graphs, etc. Let us understand with the help of an example. We will study graphs, bar graph in the next classes.
This is a collections of Naina’s toys.
PRESENTING DATA
We can present data in the form of table, pictures, graph, bar graphs, etc. Let us understand with the help of an example. We will study graphs, bar graph in the next classes.
This is a collections of Naina’s toys.
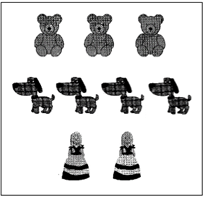 The data for Naina's toys can be represented as follows.
The data for Naina's toys can be represented as follows.
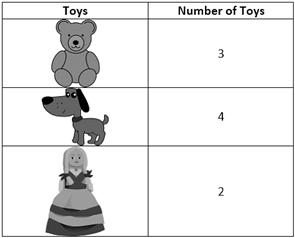 It is easier to know more...
It is easier to know more...  and
and  as money.
The currency used in India is Rupee which is denoted by symbol 'Rs.'
Money in India comes in the form of notes as well as coins. In our country, India money is the form of rupees and paise.
as money.
The currency used in India is Rupee which is denoted by symbol 'Rs.'
Money in India comes in the form of notes as well as coins. In our country, India money is the form of rupees and paise.
| Symbol used for | Symbol |
| Rupee | Rs. |
| Paise | 'p' |
 NOTES
Notes are rectangular in shape and are made up of paper. Notes can be used only for rupee. The number written on each Note tell us the value in terms of rupees.
NOTES
Notes are rectangular in shape and are made up of paper. Notes can be used only for rupee. The number written on each Note tell us the value in terms of rupees.
 COUNTING MONEY
Simple addition more...
COUNTING MONEY
Simple addition more... 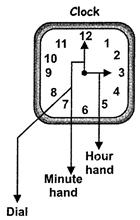 READING TIME
If someone asks you, what is the time? Then how will you answer?
Let us understand
HOW TO READ TIME?
READING TIME
If someone asks you, what is the time? Then how will you answer?
Let us understand
HOW TO READ TIME?
| Activities which take less time | Activities which take more time |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 A pattern is a repetitive design and can be seen around us.
How pattern is formed?
A pattern can be formed by using numbers, alphabets shapes or colours.
When objects or shapes are placed in an order, they form a pattern. A pattern follows a rule that allows us determine to what comes next in the sequence.
Amazing Facts
The migratory birds fly in V-Shape pattern so that they can reach the destination.
Real Life Examples:
The traffic light follows a pattern of 3 colours which repeats after few seconds to avoid traffic jam.
The pattern of white and black strip is present on the bod of zebra.
FINDING PATTERN
Where do we see Patterns in our everyday life?
We see patterns everywhere around us. For example: in the designs of a dress, in the design of an umbrella (on the basis of colours) and in the design of mehendi.
A pattern is a repetitive design and can be seen around us.
How pattern is formed?
A pattern can be formed by using numbers, alphabets shapes or colours.
When objects or shapes are placed in an order, they form a pattern. A pattern follows a rule that allows us determine to what comes next in the sequence.
Amazing Facts
The migratory birds fly in V-Shape pattern so that they can reach the destination.
Real Life Examples:
The traffic light follows a pattern of 3 colours which repeats after few seconds to avoid traffic jam.
The pattern of white and black strip is present on the bod of zebra.
FINDING PATTERN
Where do we see Patterns in our everyday life?
We see patterns everywhere around us. For example: in the designs of a dress, in the design of an umbrella (on the basis of colours) and in the design of mehendi.
 TYPES OF PATTERN
There are different types of patterns. Let us discuss them in detail.
1. NUMBER PATTERN
A list of numbers that follow certain sequence of pattern is known as number pattern
For example:
TYPES OF PATTERN
There are different types of patterns. Let us discuss them in detail.
1. NUMBER PATTERN
A list of numbers that follow certain sequence of pattern is known as number pattern
For example:
 Hence, number of pencils is increasing by the difference of 2 in each step.
Hence, number of pencils is increasing by the difference of 2 in each step.
 Same is happening in the case of example of pattern of number of butterflies shown below.
Same is happening in the case of example of pattern of number of butterflies shown below.
 2. LETTER PATTERN
Patterns can also be made with either same or different letters.
For example:
AA BB CC DO EE
A AB ABC ABCD ABCDE
A B A B A
A 5 A S A
3. COLOUR PATTERN
An arrangement of different colours to form a pattern is called a colour pattern.
For example:
2. LETTER PATTERN
Patterns can also be made with either same or different letters.
For example:
AA BB CC DO EE
A AB ABC ABCD ABCDE
A B A B A
A 5 A S A
3. COLOUR PATTERN
An arrangement of different colours to form a pattern is called a colour pattern.
For example:
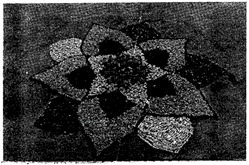 In Rangoli we use different colours to make different designs.
Historical Preview
Pattern is a particular arrangement made in different styles of numbers and various shapes and sizes.
Pattern of various designs are made on more...
In Rangoli we use different colours to make different designs.
Historical Preview
Pattern is a particular arrangement made in different styles of numbers and various shapes and sizes.
Pattern of various designs are made on more...  MEANS OF TRANSPORT
Means of transport help us to move from one place to another. There are three means of transport.
MEANS OF TRANSPORT
Means of transport help us to move from one place to another. There are three means of transport.
 (A) LAND TRANSPORT Vehicles such as cycles, rickshaw, scooters, motorcycles, cars, trucks, trains move on land only. These are known as land transport. Land transport are used to move from one city to another.
(B) WATER TRANSPORT Vehicles such as boat, ships, steamer, submarine, Yatch can move in water only. These are known as water transport.
(A) LAND TRANSPORT Vehicles such as cycles, rickshaw, scooters, motorcycles, cars, trucks, trains move on land only. These are known as land transport. Land transport are used to move from one city to another.
(B) WATER TRANSPORT Vehicles such as boat, ships, steamer, submarine, Yatch can move in water only. These are known as water transport.
 (C) AIR TRANPORT Vehicles such as aeroplane, helicopter, jet planes etc. can move in air only. These is known as air transport. Air
(C) AIR TRANPORT Vehicles such as aeroplane, helicopter, jet planes etc. can move in air only. These is known as air transport. Air
 Transport is the fastest means of transport. They cover long distances in a short time. This mode of transport is the most expensive,
COMMUNICATION
Do you feel happy when you receive a card or an e-mail wishing you 'Happy birthday?
Communication means sending or receiving messages, There are many ways by which we can communicate with people living in other places.
BY POST
A letter is a popular means of communication. We can buy land letters and postcards from a post office. We can write our messages in them and then drop them in the Post box. They reach our friends and relatives in a few days.
Urgent letters can be sent through speed post or by courier.
Historical Preview:
Dr. Marathi cooper invented the first mobile phone on 3rd April 1973.
TELEPHONE SEVIECE
The telephone is the fastest means of communication. We use a telephone to talk to our friends living within the city, in other cities more...
Transport is the fastest means of transport. They cover long distances in a short time. This mode of transport is the most expensive,
COMMUNICATION
Do you feel happy when you receive a card or an e-mail wishing you 'Happy birthday?
Communication means sending or receiving messages, There are many ways by which we can communicate with people living in other places.
BY POST
A letter is a popular means of communication. We can buy land letters and postcards from a post office. We can write our messages in them and then drop them in the Post box. They reach our friends and relatives in a few days.
Urgent letters can be sent through speed post or by courier.
Historical Preview:
Dr. Marathi cooper invented the first mobile phone on 3rd April 1973.
TELEPHONE SEVIECE
The telephone is the fastest means of communication. We use a telephone to talk to our friends living within the city, in other cities more... 

 Think
Before you choose an answer. The answer should be related to the question asked.
Think
Before you choose an answer. The answer should be related to the question asked. /15_Comprehension_(Prose_and_Poetry)_files/image001.png) QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
Comprehension means to understand. The concept of comprehension also relates to the fact of being able to answer the questions based on the passage. It is based on our ability to understand what is written in the given passage.
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
Comprehension means to understand. The concept of comprehension also relates to the fact of being able to answer the questions based on the passage. It is based on our ability to understand what is written in the given passage.

 ·
·
 ·
·




 ·
·

 ·
·
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
