| more...
Structure of Economy and Human Resource in India
Introduction
The word ?Economies? has originated from the Greek word 'Oikonomikos'; Oikos (Home)+Nomos (Management) together means 'Home Management'. Economics is a broad term referring to the scientific study of human action, particularly as it relates to human choice and the utilization of scarce resources. It includes the theories, principles, and models that deal with how the market process works. The world 'Economy' refers to an entire network of producers, distributors, and consumers of goods and services in a local, regional, or national community.
Economic Growth & Development
Increase in per capita real income in a country over a long period of time is the 'economic growth.' Economic development is defined as sustained increase in production (GDP or GNP) at 5 to 7 percent more...
Planning, Unemployment and Poverty in India
Introduction
Economic planning is the making of major economic decisions what and how much is to be produced, how, when and where it is to be produced, and to whom it is to be allocated by the comprehensive survey of the economic system as whole. (H.D. Dickinson)
 Planning in India
Planning in India starts in 1930s. Even before independence.
Subhash Chandra Bose as the President of Indian National Congress in 1938 set up a National Planning committee, Jawaharlal Nehru was appointed as its chairman. The colonial government had established a planning board that lasted from 1944 to 1946. Before independence private industrialists and economists published three development plans in 1944. India's leaders adopted the principle more...
Planning in India
Planning in India starts in 1930s. Even before independence.
Subhash Chandra Bose as the President of Indian National Congress in 1938 set up a National Planning committee, Jawaharlal Nehru was appointed as its chairman. The colonial government had established a planning board that lasted from 1944 to 1946. Before independence private industrialists and economists published three development plans in 1944. India's leaders adopted the principle more...
Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Introduction
Fiscal Policy deals with the taxation and expenditure decisions of the government covered in the annual budget.
Monetary Policy deals with the supply of money in the economy and the rate of interest. In India, the government deals with fiscal policy, while the Central bank (RBI) is responsible for monetary policy.
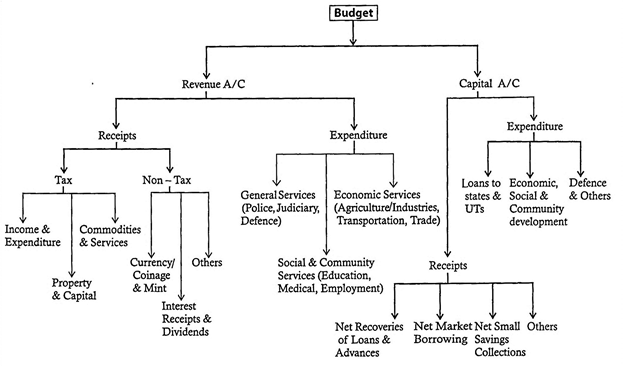 Fiscal policy
Fiscal policy or budgetary policy refers to the use by the government Finance Ministry of the various instruments such as taxation, expenditure and borrowing in order to achieve the objectives of balanced economic development, full employment and to establish a welfare state. In the context of economic liberalization, the major themes of the fiscal policy comprises:
(1) more...
Fiscal policy
Fiscal policy or budgetary policy refers to the use by the government Finance Ministry of the various instruments such as taxation, expenditure and borrowing in order to achieve the objectives of balanced economic development, full employment and to establish a welfare state. In the context of economic liberalization, the major themes of the fiscal policy comprises:
(1) more...
Money Supply and Indian Financial System
Introduction
A well-established financial system plays very important role in economic development of any country. A financial system consists of financial institutions, financial markets, financial instruments and financial services. This system provides a framework by which savings and surplus funds are mobilized in a productive manner. A financial system serves as a link between savers and investors. It promotes the capital formation by bringing together supply of savings and demand for funds.
This system provides detailed information about the players in the market such as individuals, corporate houses government agencies etc. It also provides a mechanism for controlling risks involved in managing savings and allocating funds. It covers the whole gamut of demand for and supply of funds for productive purposes. The financial system promotes economic development through more...
Business Modules & Concept in India
Introduction
Business is a concept to perform some work is an organized way for profit. It starts with a process of thinking and acting like an entrepreneur and acquiring both the theoretical and practical expertise to setup and run a company. In this chapter, different business anti ties and functioning are discusses.
Business Entities
Sole Proprietorship
Ii is an unincorporated business with one owner who pays personal income tax on profits from the business.
Partnership
A type of business organisation in which two or more individual?s pool money, skills, & other resources, & share profit & loss in accordance with terms of the partnership agreement.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
Ii is a partnership in which some or all partners have limited liabilities.
Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
Ii is an extended family more...
Industries and Infrastructure
Introduction
Growth of industries has been always focus area of the government. The reason behind this is die important role played by the industries in Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of India. The government, therefore, has many schemes and incentives to facilitate growth and development of industries. It has been generally noticed that most of the developing countries gradually move from the predominance of agriculture towards that of industries in economy as they progress on the path of economic development.
Indian economy, however portrays a contradictory trend. Here, the economic has by passed industries growth to rapid growth of services sector. The rapid growth of services may be largely attributed to reform and liberalisation of the 1990s. Indian industries contribute 18% of India's GDP and employ about 19% of work force. Major industries of our country more...
Agriculture
Introduction
Agriculture has always been one of the most important sectors of Indian economy, be it pre- independence or post- independence periods. This is further proved by the large number of Indians whose livelihood depends on griculture. Indian agriculture has a fairly successful history. It is now first in the world in the production of milk, pulses, jute and many fruits; second in rice, wheat, susarcane, cotton, etc. and a leading producer of spices, plantation crop, livestock, fishes and poultry.
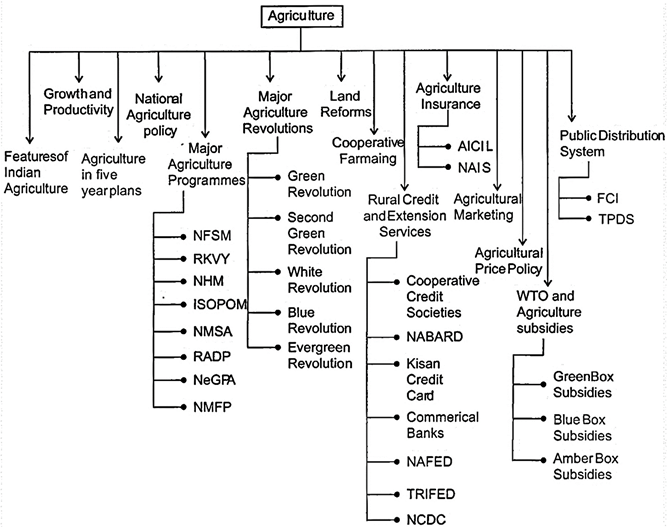 Features of Indian Agriculture
· Agriculture is the primary occupation in India. Over 58.7% rural households depend on agriculture as their principal means of livelihood. In India, 75% of below the poverty line (BPL) population lives in rural areas, and more...
Features of Indian Agriculture
· Agriculture is the primary occupation in India. Over 58.7% rural households depend on agriculture as their principal means of livelihood. In India, 75% of below the poverty line (BPL) population lives in rural areas, and more...
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |